Role of Post-Translational Modifications of cGAS in Innate Immunity
- PMID: 33105828
- PMCID: PMC7660100
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21217842
Role of Post-Translational Modifications of cGAS in Innate Immunity
Abstract
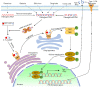
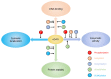
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) is the synthase that generates the second messenger cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) upon DNA binding. cGAS was first discovered as the cytosolic DNA sensor that detects DNA exposed in the cytoplasm either from pathogens or cellular damage. Activated cGAS instigates the signaling cascades to activate type I interferon (IFN) expression, critical for host defense and autoimmune diseases. In addition, cGAS plays a role in senescence, DNA repair, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. Recently, various post-translational modifications (PTMs) of cGAS have been reported, such as phosphorylation, ubiquitination, acetylation, glutamylation, and sumoylation. These PTMs profoundly affect cGAS functions. Thus, here we review the recent reported PTMs of cGAS and how these PTMs regulate cGAS enzymatic activity, DNA binding, and protein stability, and discuss the potential future directions.
Keywords: acetylation; cGAS; glutamylation; innate immunity; phosphorylation; post-translational modification; sumoylation; ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Advances in post-translational modifications of cGAS in innate immunity].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Feb;40(2):179-185. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38284260 Chinese.
-
The DNA Sensor cGAS is Decorated by Acetylation and Phosphorylation Modifications in the Context of Immune Signaling.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Jul;19(7):1193-1208. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA120.001981. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32345711 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational regulation of antiviral innate signaling.Eur J Immunol. 2017 Sep;47(9):1414-1426. doi: 10.1002/eji.201746959. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Eur J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28744851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-translational modification control of viral DNA sensors and innate immune signaling.Adv Virus Res. 2021;109:163-199. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2021.03.001. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Adv Virus Res. 2021. PMID: 33934827 Free PMC article.
-
cGAS-STING pathway: post-translational modifications and functions in sterile inflammatory diseases.FEBS J. 2022 Oct;289(20):6187-6208. doi: 10.1111/febs.16137. Epub 2021 Aug 1. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34310043 Review.
Cited by
-
cGAMP-activated cGAS-STING signaling: its bacterial origins and evolutionary adaptation by metazoans.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023 Mar;30(3):245-260. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-00933-9. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36894694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccinia E5 is a major inhibitor of the DNA sensor cGAS.Nat Commun. 2023 May 22;14(1):2898. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38514-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37217469 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) inhibits coronavirus infection by disrupting viral replication organelles.J Med Virol. 2024 Nov;96(11):e70020. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70020. J Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 39470032
-
The efficient synthesis and purification of 2'3'- cGAMP from Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 8;15:1345617. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1345617. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38525075 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the cGAS-STING pathway in systemic and organ-specific diseases.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022 Sep;18(9):558-572. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00589-6. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35732833 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang X., Wu J.X., Du F.H., Xu H., Sun L.J., Chen Z., Brautigam C.A., Zhang X.W., Chen Z.J.J. The Cytosolic DNA Sensor cGAS Forms an Oligomeric Complex with DNA and Undergoes Switch-like Conformational Changes in the Activation Loop. Cell Rep. 2014;6:421–430. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.01.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous