The Long Non-coding RNAs: Paramount Regulators of the NLRP3 Inflammasome
- PMID: 33101288
- PMCID: PMC7546312
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.569524
The Long Non-coding RNAs: Paramount Regulators of the NLRP3 Inflammasome
Abstract
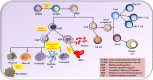
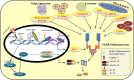
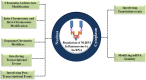
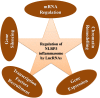
The NOD LRR pyrin domain containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is a cytosolic multi-proteins conglomerate with intrinsic ATPase activity. Their predominant presence in the immune cells emphasizes its significant role in immune response. The downstream effector proteins IL-1β and IL-18 are responsible for the biological functions of the NLRP3 inflammasome upon encountering the alarmins and microbial ligands. Although the NLRP3 inflammasome is essential for host defense during infections, uncontrolled activation and overproduction of IL-1β and IL-18 increase the risk of developing autoimmune and metabolic disorders. Emerging evidences suggest the action of lncRNAs in regulating the activity of NLRP3 inflammasome in various disease conditions. The long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is an emerging field of study and evidence on their regulatory role in various diseases is grabbing attention. Recent studies emphasize the functions of lncRNAs in the fine control of the NLRP3 inflammasome at nuclear and cytoplasmic levels by interfering in chromatin architecture, gene transcription and translation. Recently, lncRNAs are also found to control the activity of various regulators of NLRP3 inflammasome. Understanding the precise role of lncRNA in controlling the activity of NLRP3 inflammasome helps us to design targeted therapies for multiple inflammatory diseases. The present review is a novel attempt to consolidate the substantial role of lncRNAs in the regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. A deeper insight on the NLRP3 inflammasome regulation by lncRNAs will help in developing targeted and beneficial therapeutics in the future.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; chromatin remodeling; cytoplasmic regulation; decoys; lncRNAs; nuclear regulation; scaffolds; transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2020 Menon and Hua.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-coding RNAs: The key regulators in NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Nov;100:108105. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108105. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34481143 Review.
-
Regulation of NLRP3 by non-coding RNAs in different cancers: interplay between non-coding RNAs and NLRP3 in carcinogenesis and metastasis.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020 Dec 31;66(8):47-51. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020. PMID: 34174977 Review.
-
Human NACHT, LRR, and PYD domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activity is regulated by and potentially targetable through Bruton tyrosine kinase.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Oct;140(4):1054-1067.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.017. Epub 2017 Feb 16. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28216434
-
NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in atherosclerosis: Focusing on the therapeutic potential of non-coding RNAs.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Jun;246:154490. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154490. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37141699 Review.
-
MicroRNAs as important regulators of the NLRP3 inflammasome.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020 Jan;150:50-61. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31100298 Review.
Cited by
-
NEAT1 and MALAT1 are highly expressed in saliva and nasopharyngeal swab samples of COVID-19 patients.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2021 Dec;36(6):291-294. doi: 10.1111/omi.12351. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34463043 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of Noncoding RNAs in Bovine Mastitis Diseases.Pathogens. 2022 Sep 3;11(9):1009. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11091009. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36145441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) NEAT1 and MALAT1 are differentially expressed in severe COVID-19 patients: An integrated single cell analysis.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Jul 31:2021.03.26.21254445. doi: 10.1101/2021.03.26.21254445. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: PLoS One. 2022 Jan 10;17(1):e0261242. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261242. PMID: 33821282 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Non-coding RNAs as a Critical Player in the Regulation of Inflammasome in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases; Emphasize on lncRNAs.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Oct 19. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01585-2. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 39424765 Review.
-
Targeting Inflammasome Activation in COVID-19: Delivery of RNA Interference-Based Therapeutic Molecules.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 3;9(12):1823. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121823. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34944639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

