A large-scale genome-wide association study meta-analysis of cannabis use disorder
- PMID: 33096046
- PMCID: PMC7674631
- DOI: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30339-4
A large-scale genome-wide association study meta-analysis of cannabis use disorder
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Psychiatry 2020; 7: 1032-45.Lancet Psychiatry. 2022 Apr;9(4):e12. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(22)00065-7. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35219447 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Variation in liability to cannabis use disorder has a strong genetic component (estimated twin and family heritability about 50-70%) and is associated with negative outcomes, including increased risk of psychopathology. The aim of the study was to conduct a large genome-wide association study (GWAS) to identify novel genetic variants associated with cannabis use disorder.
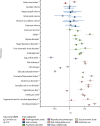
Methods: To conduct this GWAS meta-analysis of cannabis use disorder and identify associations with genetic loci, we used samples from the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium Substance Use Disorders working group, iPSYCH, and deCODE (20 916 case samples, 363 116 control samples in total), contrasting cannabis use disorder cases with controls. To examine the genetic overlap between cannabis use disorder and 22 traits of interest (chosen because of previously published phenotypic correlations [eg, psychiatric disorders] or hypothesised associations [eg, chronotype] with cannabis use disorder), we used linkage disequilibrium score regression to calculate genetic correlations.
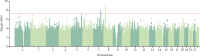
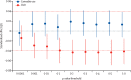
Findings: We identified two genome-wide significant loci: a novel chromosome 7 locus (FOXP2, lead single-nucleotide polymorphism [SNP] rs7783012; odds ratio [OR] 1·11, 95% CI 1·07-1·15, p=1·84 × 10-9) and the previously identified chromosome 8 locus (near CHRNA2 and EPHX2, lead SNP rs4732724; OR 0·89, 95% CI 0·86-0·93, p=6·46 × 10-9). Cannabis use disorder and cannabis use were genetically correlated (rg 0·50, p=1·50 × 10-21), but they showed significantly different genetic correlations with 12 of the 22 traits we tested, suggesting at least partially different genetic underpinnings of cannabis use and cannabis use disorder. Cannabis use disorder was positively genetically correlated with other psychopathology, including ADHD, major depression, and schizophrenia.
Interpretation: These findings support the theory that cannabis use disorder has shared genetic liability with other psychopathology, and there is a distinction between genetic liability to cannabis use and cannabis use disorder.
Funding: National Institute of Mental Health; National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism; National Institute on Drug Abuse; Center for Genomics and Personalized Medicine and the Centre for Integrative Sequencing; The European Commission, Horizon 2020; National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; Health Research Council of New Zealand; National Institute on Aging; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; UK Research and Innovation Medical Research Council (UKRI MRC); The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation; National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders; Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA); National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering; National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Australia; Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program of the University of California; Families for Borderline Personality Disorder Research (Beth and Rob Elliott) 2018 NARSAD Young Investigator Grant; The National Child Health Research Foundation (Cure Kids); The Canterbury Medical Research Foundation; The New Zealand Lottery Grants Board; The University of Otago; The Carney Centre for Pharmacogenomics; The James Hume Bequest Fund; National Institutes of Health: Genes, Environment and Health Initiative; National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute; The William T Grant Foundation; Australian Research Council; The Virginia Tobacco Settlement Foundation; The VISN 1 and VISN 4 Mental Illness Research, Education, and Clinical Centers of the US Department of Veterans Affairs; The 5th Framework Programme (FP-5) GenomEUtwin Project; The Lundbeck Foundation; NIH-funded Shared Instrumentation Grant S10RR025141; Clinical Translational Sciences Award grants; National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Using genetic information to inform policy on cannabis.Lancet Psychiatry. 2020 Dec;7(12):1002-1003. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30377-1. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33096047 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide association study meta-analysis of dizygotic twinning illuminates genetic regulation of female fecundity.Hum Reprod. 2024 Jan 5;39(1):240-257. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dead247. Hum Reprod. 2024. PMID: 38052102 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies three novel loci for circulating anti-Müllerian hormone levels in women.Hum Reprod. 2022 May 3;37(5):1069-1082. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deac028. Hum Reprod. 2022. PMID: 35274129 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between cannabis use, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder: a genetically informed study.Lancet Psychiatry. 2023 Jun;10(6):441-451. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(23)00143-8. Lancet Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37208114 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel risk loci for restless legs syndrome in genome-wide association studies in individuals of European ancestry: a meta-analysis.Lancet Neurol. 2017 Nov;16(11):898-907. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30327-7. Lancet Neurol. 2017. PMID: 29029846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence Brief: The Quality of Care Provided by Advanced Practice Nurses [Internet].Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 Sep. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 Sep. PMID: 27606392 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic structural equation modeling reveals latent phenotypes in the human cortex with distinct genetic architecture.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 24;14(1):451. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-03152-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39448598 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabis and Psychosis: Weeding Out Fact from Fiction.Mo Med. 2024 Sep-Oct;121(5):333-339. Mo Med. 2024. PMID: 39421474 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cannabis use disorder increases risk of large-artery atherosclerotic stroke and migraine with aura through mendelian randomization study.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 16;14(1):24295. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74754-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39414896 Free PMC article.
-
Methylomic signature of current cannabis use in two first-episode psychosis cohorts.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 16. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02689-0. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39406996
-
Cannabis use disorder: from neurobiology to treatment.J Clin Invest. 2024 Oct 15;134(20):e172887. doi: 10.1172/JCI172887. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39403927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21 AA027827/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH048085/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA005147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016977/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA005147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DA028909/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA036216/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA032555/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA041147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA009367/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA032573/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH080230/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA035804/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA007535/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061162/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD031921/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041120/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA014041/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 AA017688/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N01HG65403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA009367/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DC018098/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AA017828/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011998/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH063970/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD060726/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA007728/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA024413/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041093/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA021905/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH118233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA021913/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD073342/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA017444/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 MH122058/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA041123/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH117559/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025141/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S035818/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DA051038/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA047527/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA019157/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA024413/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA012854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041134/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041022/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA046791/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH068521/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA024417/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA026911/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013321/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041156/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA025109/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG008983/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD093651/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA034076/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HD097630/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17209/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DA042755/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA024417/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD050735/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004422/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA038504/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041025/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA023026/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA019963/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013423/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH109514/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD074711/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA022537/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH066140/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012845/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041089/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AA018755/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041106/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007261/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115305/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00007/10/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268200782096C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DA023549/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DA019951/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041117/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA017535/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH093731/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA037904/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA017305/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041028/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041048/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025092/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006378/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH113848/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018673/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH109532/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041148/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH018951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083094/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DA011301/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AA027435/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS032830/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011408/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004798/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P2C HD066613/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA007728/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH063671/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH123619/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 MH120736/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA044283/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041174/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013320/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DA011015/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013240/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA005605/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

