Urgent need of rapid tests for SARS CoV-2 antigen detection: Evaluation of the SD-Biosensor antigen test for SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33053494
- PMCID: PMC7522649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104654
Urgent need of rapid tests for SARS CoV-2 antigen detection: Evaluation of the SD-Biosensor antigen test for SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
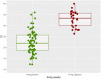
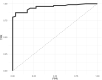
At the time of writing, FIND has listed four CE-marked SARSCoV-2 antigen tests. We evaluated the recently CE-approved rapid POCT SD-Biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein detection in nasopharyngeal secretions from 330 patients admitted to the Emergency Room for a suspect of COVID-19 and travelers returning home from high risk countries. Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, negative and predictive values were consistent with the use of the test to mass-screening for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance.
Keywords: Antigen test; Cell culture; Mass-screening; Point-of-care-testing; Sars CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Performance evaluation of a lateral flow assay for nasopharyngeal antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 May;35(5):e23745. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23745. Epub 2021 Mar 5. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33675086 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay-based high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for the diagnosis of COVID-19: The VITROS® SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test.J Med Virol. 2021 Dec;93(12):6778-6781. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27153. Epub 2021 Aug 12. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 34170555 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of Panbio and SD Biosensor antigen rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 diagnosis.J Med Virol. 2021 Sep;93(9):5650-5654. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27089. Epub 2021 May 31. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 34002864 Free PMC article.
-
State of the Art on the SARS-CoV-2 Toolkit for Antigen Detection: One Year Later.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 31;11(9):310. doi: 10.3390/bios11090310. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34562898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status of the lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swabs.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2021 Jun 15;31(2):020601. doi: 10.11613/BM.2021.020601. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2021. PMID: 34140830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Performance of the RT-LAMP-based eazyplex® SARS-CoV-2 as a novel rapid diagnostic test.J Clin Virol. 2021 May;138:104817. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104817. Epub 2021 Apr 1. J Clin Virol. 2021. PMID: 33836452 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Testing With Contact Tracing Compared to Test and Trace for the Effective Suppression of COVID-19 in the United Kingdom: Systematic Review.JMIRx Med. 2021 Apr 12;2(2):e27254. doi: 10.2196/27254. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. JMIRx Med. 2021. PMID: 33857269 Free PMC article.
-
Performance characteristics of five antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic test (Ag-RDT) for SARS-CoV-2 asymptomatic infection: a head-to-head benchmark comparison.J Infect. 2021 Jun;82(6):269-275. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.04.009. Epub 2021 Apr 18. J Infect. 2021. PMID: 33882299 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Nasal Cavity and Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens for SARS-CoV-2 Detection via Rapid Antigen Test According to Specimen Collection Timing and Viral Load.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 14;12(3):710. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030710. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328263 Free PMC article.
-
Perception of COVID-19 Testing in the Entire Population.Front Public Health. 2022 Feb 10;10:757065. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.757065. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35223721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corman V.M., Landt O., Kaiser M., Molenkamp R., Meijer A., Chu D.K., et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance [Internet] 2020;25(3) https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.... Jan 23 [cited 2020 Feb 11]. Available from: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

