Extrafollicular B cell responses correlate with neutralizing antibodies and morbidity in COVID-19
- PMID: 33028979
- PMCID: PMC7739702
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-00814-z
Extrafollicular B cell responses correlate with neutralizing antibodies and morbidity in COVID-19
Abstract
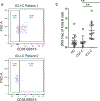
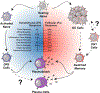
A wide spectrum of clinical manifestations has become a hallmark of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) COVID-19 pandemic, although the immunological underpinnings of diverse disease outcomes remain to be defined. We performed detailed characterization of B cell responses through high-dimensional flow cytometry to reveal substantial heterogeneity in both effector and immature populations. More notably, critically ill patients displayed hallmarks of extrafollicular B cell activation and shared B cell repertoire features previously described in autoimmune settings. Extrafollicular activation correlated strongly with large antibody-secreting cell expansion and early production of high concentrations of SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing antibodies. Yet, these patients had severe disease with elevated inflammatory biomarkers, multiorgan failure and death. Overall, these findings strongly suggest a pathogenic role for immune activation in subsets of patients with COVID-19. Our study provides further evidence that targeted immunomodulatory therapy may be beneficial in specific patient subpopulations and can be informed by careful immune profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
F.E.-H.L. is the founder of MicroB-plex and has research grants with Genentech. W.T.H. has consulted for ViveBio, AARP and Biogen; has received research support from Fujirebio; and has a patent on CSF-based diagnosis of FTLD-TDP. M.S.D. is a consultant for Inbios, Vir Biotechnology and NGM Biopharmaceuticals and is on the scientific advisory board of Moderna. The Diamond laboratory has received unrelated funding support in sponsored research agreements from Moderna, Vir Biotechnology and Emergent BioSolutions. J.E.C. has served as a consultant for Pfizer, Novavax, Lilly and Luna Biologics; is a member of the scientific advisory boards of CompuVax and Meissa Vaccines; and is Founder of IDBiologics. The Crowe laboratory at Vanderbilt University Medical Center has received unrelated funding support in sponsored research agreements from Moderna, Sanofi-Aventis and IDBiologics.
Figures

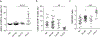






Update of
-
Dominant extrafollicular B cell responses in severe COVID-19 disease correlate with robust viral-specific antibody production but poor clinical outcomes.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jun 22:2020.04.29.20083717. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.29.20083717. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nat Immunol. 2020 Dec;21(12):1506-1516. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-00814-z. PMID: 32511635 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Dominant extrafollicular B cell responses in severe COVID-19 disease correlate with robust viral-specific antibody production but poor clinical outcomes.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jun 22:2020.04.29.20083717. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.29.20083717. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nat Immunol. 2020 Dec;21(12):1506-1516. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-00814-z. PMID: 32511635 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Expansion of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody-Secreting Cells and Generation of Neutralizing Antibodies in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients.J Immunol. 2020 Nov 1;205(9):2437-2446. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000717. Epub 2020 Sep 2. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32878912 Free PMC article.
-
Landscapes and dynamic diversifications of B-cell receptor repertoires in COVID-19 patients.Hum Immunol. 2022 Feb;83(2):119-129. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2021.10.007. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Hum Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34785098 Free PMC article.
-
Follicular Helper T Cells in the Immunopathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 16;12:731100. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731100. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34603308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: Significance of antibodies.Hum Antibodies. 2020;28(4):287-297. doi: 10.3233/HAB-200429. Hum Antibodies. 2020. PMID: 32986664 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding autoimmune response after SARS-CoV-2 infection and the pathogenesis/mechanisms of long COVID.Med Rev (2021). 2024 May 27;4(5):367-383. doi: 10.1515/mr-2024-0013. eCollection 2024 Oct. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 39444797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extrafollicular CD19lowCXCR5-CD11c- double negative 3 (DN3) B cells are significantly associated with disease activity in females with systemic lupus erythematosus.J Transl Autoimmun. 2024 Oct 9;9:100252. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2024.100252. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Transl Autoimmun. 2024. PMID: 39444662 Free PMC article.
-
Causal relationship between circulating immune cells and gastric cancer: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis using UK Biobank and FinnGen datasets.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):4702-4713. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-480. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39430856 Free PMC article.
-
Hypophysitis in COVID-19: a systematic review.Pituitary. 2024 Oct 15. doi: 10.1007/s11102-024-01462-4. Online ahead of print. Pituitary. 2024. PMID: 39404935 Review.
-
Risk of systemic lupus erythematosus flare after COVID-19 hospitalization: A matched cohort study.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 10;19(10):e0309316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309316. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39388388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harrison C Focus shifts to antibody cocktails for COVID-19 cytokine storm. Nat. Biotechnol 38, 905–908 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

