Topologically selective islet vulnerability and self-sustained downregulation of markers for β-cell maturity in streptozotocin-induced diabetes
- PMID: 32999405
- PMCID: PMC7527346
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-01243-2
Topologically selective islet vulnerability and self-sustained downregulation of markers for β-cell maturity in streptozotocin-induced diabetes
Abstract
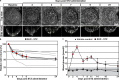
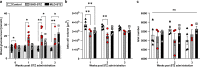
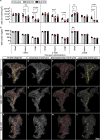
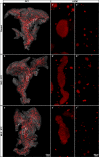
Mouse models of Streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetes represent the most widely used preclinical diabetes research systems. We applied state of the art optical imaging schemes, spanning from single islet resolution to the whole organ, providing a first longitudinal, 3D-spatial and quantitative account of β-cell mass (BCM) dynamics and islet longevity in STZ-treated mice. We demonstrate that STZ-induced β-cell destruction predominantly affects large islets in the pancreatic core. Further, we show that hyperglycemic STZ-treated mice still harbor a large pool of remaining β-cells but display pancreas-wide downregulation of glucose transporter type 2 (GLUT2). Islet gene expression studies confirmed this downregulation and revealed impaired β-cell maturity. Reversing hyperglycemia by islet transplantation partially restored the expression of markers for islet function, but not BCM. Jointly our results indicate that STZ-induced hyperglycemia results from β-cell dysfunction rather than β-cell ablation and that hyperglycemia in itself sustains a negative feedback loop restraining islet function recovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Author P.O.B. is founder and CEO of Biocrine AB, Sweden and author E.I. is consultant for Biocrine AB. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterizing pancreatic β-cell heterogeneity in the streptozotocin model by single-cell transcriptomic analysis.Mol Metab. 2020 Jul;37:100982. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.100982. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32247924 Free PMC article.
-
KATP channel-deficient pancreatic beta-cells are streptozotocin resistant because of lower GLUT2 activity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Feb;294(2):E326-35. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00296.2007. Epub 2007 Nov 27. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18042662
-
Islet remodeling in female mice with spontaneous autoimmune and streptozotocin-induced diabetes.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 7;9(8):e102843. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102843. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25101835 Free PMC article.
-
β-Cell keratin 8 maintains islet mechanical integrity, mitochondrial ultrastructure, and β-cell glucose transporter 2 plasma membrane targeting.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Aug 1;327(2):C462-C476. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00123.2024. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38912736
-
Dynamic pathology of islet endocrine cells in type 2 diabetes: β-Cell growth, death, regeneration and their clinical implications.J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Mar;7(2):155-65. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12424. Epub 2015 Oct 15. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27042265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreas Optical Clearing and 3-D Microscopy in Health and Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 26;12:644826. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.644826. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33981285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic loss of Mig6 alters murine endocrine cell fate and protects functional beta cell mass in an STZ-induced model of diabetes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 8:2023.04.07.536046. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.07.536046. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37066257 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Guidelines on models of diabetic heart disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Jul 1;323(1):H176-H200. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00058.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35657616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Eye as a Transplantation Site to Monitor Pancreatic Islet Cell Plasticity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 23;12:652853. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.652853. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33967961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geometric and topological characterization of the cytoarchitecture of islets of Langerhans.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Nov 9;19(11):e1011617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011617. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37943957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlqvist E, et al. Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: a data-driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:361–369. - PubMed
-
- Lenzen S. The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia. 2008;51:216–226. - PubMed
-
- Tjalve H, Wilander E, Johansson EB. Distribution of labelled streptozotocin in mice: uptake and retention in pancreatic islets. J. Endocrinol. 1976;69:455–456. - PubMed
-
- Radenkovic M, Stojanovic M, Prostran M. Experimental diabetes induced by alloxan and streptozotocin: the current state of the art. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods. 2016;78:13–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

