Temporal Detection and Phylogenetic Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 in Municipal Wastewater
- PMID: 32904687
- PMCID: PMC7457911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100098
Temporal Detection and Phylogenetic Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 in Municipal Wastewater
Abstract
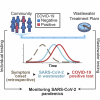
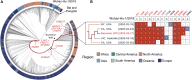
SARS-CoV-2 has recently been detected in feces, which indicates that wastewater may be used to monitor viral prevalence in the community. Here, we use RT-qPCR to monitor wastewater for SARS-CoV-2 RNA over a 74-day time course. We show that changes in SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentrations follow symptom onset gathered by retrospective interview of patients but precedes clinical test results. In addition, we determine a nearly complete (98.5%) SARS-CoV-2 genome sequence from wastewater and use phylogenetic analysis to infer viral ancestry. Collectively, this work demonstrates how wastewater can be used as a proxy to monitor viral prevalence in the community and how genome sequencing can be used for genotyping viral strains circulating in a community.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; genome sequencing; wastewater-based epidemiology.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
B.W. is the founder of SurGene and VIRIS Detection Systems, and is an inventor on patent applications related to CRISPR-Cas systems and applications thereof.
Figures

Update of
-
Temporal detection and phylogenetic assessment of SARS-CoV-2 in municipal wastewater.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 5:2020.04.15.20066746. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.15.20066746. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell Rep Med. 2020 Sep 22;1(6):100098. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100098. PMID: 32511611 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Temporal detection and phylogenetic assessment of SARS-CoV-2 in municipal wastewater.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 5:2020.04.15.20066746. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.15.20066746. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell Rep Med. 2020 Sep 22;1(6):100098. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100098. PMID: 32511611 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Wastewater-Based SARS-CoV-2 Surveillance in Northern New England.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0220721. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02207-21. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35412387 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking community infection dynamics of COVID-19 by monitoring SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater, counting positive reactions by qPCR.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Dec 15;904:166420. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166420. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 37611711
-
Development of highly sensitive one-step reverse transcription-quantitative PCR for SARS-CoV-2 detection in wastewater.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Jan 10;907:167844. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167844. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 37852499
-
Comparison of the methods for isolation and detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in municipal wastewater.Front Public Health. 2023 Mar 7;11:1116636. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1116636. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36960362 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessing RNA integrity by digital RT-PCR: Influence of extraction, storage, and matrices.Biol Methods Protoc. 2024 Jul 27;9(1):bpae053. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpae053. eCollection 2024. Biol Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39450241 Free PMC article.
-
The Detection of Periodic Reemergence Events of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Strain in Communities Dominated by Omicron.Pathogens. 2022 Oct 28;11(11):1249. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11111249. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36365000 Free PMC article.
-
Viruses in wastewater: occurrence, abundance and detection methods.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Nov 25;745:140910. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140910. Epub 2020 Jul 19. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32758747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Nanopore and Synthesis-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Platforms for SARS-CoV-2 Variant Monitoring in Wastewater.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 6;24(24):17184. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417184. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139015 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of various viruses and recent evidence of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater systems.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Jul 15;414:125439. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125439. Epub 2021 Feb 19. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 33684818 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2020. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report - 1.https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

