Gelling hypotonic polymer solution for extended topical drug delivery to the eye
- PMID: 32895514
- PMCID: PMC7655548
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-020-00606-8
Gelling hypotonic polymer solution for extended topical drug delivery to the eye
Abstract
Eye-drop formulations should hold as high a concentration of soluble drug in contact with ocular epithelium for as long as possible. However, eye tears and frequent blinking limit drug retention on the ocular surface, and gelling drops typically form clumps that blur vision. Here, we describe a gelling hypotonic solution containing a low concentration of a thermosensitive triblock copolymer for extended ocular drug delivery. On topical application, the hypotonic formulation forms a highly uniform and clear thin layer that conforms to the ocular surface and resists clearance from blinking, increasing the intraocular absorption of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs and extending the drug-ocular-epithelium contact time with respect to conventional thermosensitive gelling formulations and commercial eye drops. We also show that the conformal gel layer allows for therapeutically relevant drug delivery to the posterior segment of the eyeball in pigs. Our findings highlight the importance of formulations that conform to the ocular surface before viscosity enhancement for increased and prolonged ocular surface contact and drug absorption.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
Y.C.K., A.D., L.E., and J.H. are inventors on patents/patent applications related to this technology.
Figures
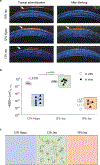


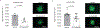
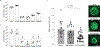
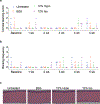
Comment in
-
A topical gel for extended ocular drug release.Nat Biomed Eng. 2020 Nov;4(11):1024-1025. doi: 10.1038/s41551-020-00645-1. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 33159191 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Comparison of thermosensitive in situ gels and drug-resin complex for ocular drug delivery: In vitro drug release and in vivo tissue distribution.Int J Pharm. 2020 Mar 30;578:119184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119184. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32112932
-
Comparison of ion-activated in situ gelling systems for ocular drug delivery. Part 1: physicochemical characterisation and in vitro release.Int J Pharm. 2011 Jun 15;411(1-2):69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.03.042. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Int J Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21453762
-
Novel in situ gelling ophthalmic drug delivery system based on gellan gum and hydroxyethylcellulose: Innovative rheological characterization, in vitro and in vivo evidence of a sustained precorneal retention time.Int J Pharm. 2020 Jan 25;574:118734. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118734. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31705970
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of in situ gelling systems for sustained topical ophthalmic delivery: state of the art and beyond.Drug Discov Today. 2017 Apr;22(4):638-651. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Drug Discov Today. 2017. PMID: 28017837 Review.
-
Chitosan-Based In Situ Gels for Ocular Delivery of Therapeutics: A State-of-the-Art Review.Mar Drugs. 2018 Oct 9;16(10):373. doi: 10.3390/md16100373. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30304825 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ion-Complex Microcrystal Formulation Provides Sustained Delivery of a Multimodal Kinase Inhibitor from the Subconjunctival Space for Protection of Retinal Ganglion Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2021 May 1;13(5):647. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050647. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34062883 Free PMC article.
-
Intelligent Hydrogels in Myocardial Regeneration and Engineering.Gels. 2022 Sep 9;8(9):576. doi: 10.3390/gels8090576. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36135287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypotonic, gel-forming delivery system for vaginal drug administration.J Control Release. 2024 Jul;371:101-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.05.037. Epub 2024 May 24. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 38782065
-
Engineered peptide-drug conjugate provides sustained protection of retinal ganglion cells with topical administration in rats.J Control Release. 2023 Oct;362:371-380. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.08.058. Epub 2023 Sep 4. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37657693 Free PMC article.
-
Dendrimer and dendrimer gel-derived drug delivery systems: Breaking bottlenecks of topical administration of glaucoma medications.MedComm Biomater Appl. 2023 Mar;2(1):e30. doi: 10.1002/mba2.30. Epub 2023 Feb 20. MedComm Biomater Appl. 2023. PMID: 38562247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Urtti A, Pipkin JD, Rork G & Repta AJ Controlled Drug Delivery Devices for Experimental Ocular Studies with Timolol .1. Invitro Release Studies. Int J Pharm 61, 235–240, doi:Doi 10.1016/0378-5173(90)90214-O (1990). - DOI
-
- Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Owen S. n. C. & American Pharmacists Association. Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients / edited by Rowe Raymond C., Sheskey Paul J., Quinn Marian E.. 6th edn, (APhA/Pharmaceutical Press;, 2009).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

