HDAC6 regulates antibody-dependent intracellular neutralization of viruses via deacetylation of TRIM21
- PMID: 32796032
- PMCID: PMC7573261
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011006
HDAC6 regulates antibody-dependent intracellular neutralization of viruses via deacetylation of TRIM21
Abstract
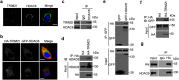
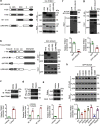
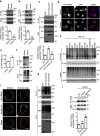
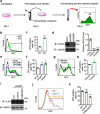
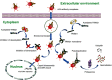
Tripartite motif-containing protein 21 (TRIM21) is a cytosolic antibody receptor that targets the internalized virus-antibody complex to the proteasome for degradation. However, the precise mechanism regulating TRIM21 activity is unknown. Here we show that TRIM21 is a substrate of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) and that its function is regulated by acetylation. HDAC6 interacts with TRIM21 through its PRYSPRY motif and deacetylates TRIM21 at lysine 385 and lysine 387, thus promoting its homodimerization. Inhibiting HDAC6 activity increases TRIM21 acetylation, and hyperacetylation blocks TRIM21 dimerization and ubiquitination, preventing its binding to the virus-antibody complex and its degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. HDAC6 depletion or inhibition increases virus accumulation in cells, indicative of an impaired capacity for antibody-dependent intracellular neutralization of viruses, whereas TRIM21 acetylation-deficient K385/387R mutant rescues HDAC6 depletion-caused ADIN impairment. These findings provide evidence for HDAC6 as a novel regulator of TRIM21-mediated intracellular innate immunity.
Keywords: HDAC6; TRIM21; acetylation; antibody-dependent intracellular neutralization; histone deacetylase 6; infection; virus.
© 2020 Xie et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of virus neutralization and the persistent fraction by TRIM21.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(16):8482-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00728-12. Epub 2012 May 30. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22647693 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) deacetylates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) and thereby stimulates ERK1 activity.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 9;293(6):1976-1993. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.795955. Epub 2017 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29259132 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM21-dependent intracellular antibody neutralization of virus infection.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;129:167-87. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 25595804 Review.
-
TRIM21-From Intracellular Immunity to Therapy.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 28;10:2049. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02049. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31555278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translocalized IgA mediates neutralization and stimulates innate immunity inside infected cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Sep 16;111(37):13463-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1410980111. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25169018 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of TRIM21/Ro52 in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 6;15:1435525. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1435525. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39165359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxoplasma gondii Type-I ROP18 Targeting Human E3 Ligase TRIM21 for Immune Escape.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 26;9:685913. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.685913. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34124071 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM21/Ro52 - Roles in Innate Immunity and Autoimmune Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 6;12:738473. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.738473. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34552597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDAC6 deacetylates IDH1 to promote the homeostasis of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.EMBO Rep. 2023 Oct 9;24(10):e56009. doi: 10.15252/embr.202256009. Epub 2023 Aug 29. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37642636 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM21 reduces H1N1-induced inflammation and apoptosis by regulating the TBK1-IRF3 signaling pathway in A549 cells.Arch Virol. 2024 Mar 13;169(4):74. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-05989-6. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 38480558
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

