PROTACs: An Emerging Therapeutic Modality in Precision Medicine
- PMID: 32795419
- PMCID: PMC9424844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.07.020
PROTACs: An Emerging Therapeutic Modality in Precision Medicine
Abstract
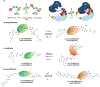
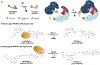
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) has emerged as an exciting new era in chemical biology and drug discovery. PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) technology targets cellular proteins for degradation by co-opting the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Over the last 5 years, numerous studies have expanded our understanding of the unique mode of action and advantages of PROTACs, which has in turn spurred interest in both academia and industry to explore PROTACs as a novel therapeutic strategy. In this review, we first highlight the key advantages of PROTACs and then discuss the spatiotemporal regulation of protein degradation. Next, we explore current chemically tractable E3 ligases focusing on expanding the existing repertoire with novel E3 ligases to uncover the full potential of TPD. Collectively, these studies are guiding the development of the PROTAC technology as it emerges as a new modality in precision medicine.
Keywords: E3 ligase; PROTACs; PhotoPROTACs; covalent ligands; proteasome; targeted protein degradation.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests C.M.C. is founder, shareholder, and consultant to Arvinas, Inc. and Halda, LLC, which support research in his laboratory.
Figures
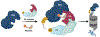

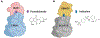
Similar articles
-
PROTAC-DB 2.0: an updated database of PROTACs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D1367-D1372. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac946. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36300631 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of E3 Ligase Ligands for Target Protein Degradation.Molecules. 2022 Oct 2;27(19):6515. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196515. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) in cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2022 Apr 11;21(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01434-3. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35410300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Major advances in targeted protein degradation: PROTACs, LYTACs, and MADTACs.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100647. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100647. Epub 2021 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33839157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E3 Ligase Ligands for PROTACs: How They Were Found and How to Discover New Ones.SLAS Discov. 2021 Apr;26(4):484-502. doi: 10.1177/2472555220965528. Epub 2020 Nov 3. SLAS Discov. 2021. PMID: 33143537 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitination and deubiquitination in cancer: from mechanisms to novel therapeutic approaches.Mol Cancer. 2024 Jul 25;23(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02046-3. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39048965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cIAP1-based degraders induce degradation via branched ubiquitin architectures.Nat Chem Biol. 2023 Mar;19(3):311-322. doi: 10.1038/s41589-022-01178-1. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Nat Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 36316570
-
Acute pharmacological degradation of ERK5 does not inhibit cellular immune response or proliferation.Cell Chem Biol. 2022 Nov 17;29(11):1630-1638.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2022.09.004. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Cell Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 36220104 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted MDM2 Degradation Reveals a New Vulnerability for p53-Inactivated Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2023 May 4;13(5):1210-1229. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-1131. Cancer Discov. 2023. PMID: 36734633 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in PROTAC-Based Antiviral Strategies.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 27;11(2):270. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020270. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851148 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albert L, and Vázquez O.(2019). Photoswitchable peptides for spatiotemporal control of biological functions. Chemical Communications 55, 10192–10213. - PubMed
-
- Asatsuma-Okumura T, Ando H, De Simone M, Yamamoto J, Sato T, Shimizu N, Asakawa K, Yamaguchi Y, Ito T, Guerrini L, et al. (2019). p63 is a cereblon substrate involved in thalidomide teratogenicity. Nature Chemical Biology 15, 1077–1084. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

