Upregulation of circ_0000199 in circulating exosomes is associated with survival outcome in OSCC
- PMID: 32792549
- PMCID: PMC7426867
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-70747-y
Upregulation of circ_0000199 in circulating exosomes is associated with survival outcome in OSCC
Abstract
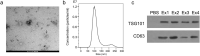
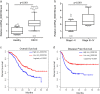
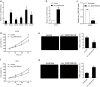
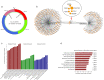
Studies have found that circRNA in exosomes is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) progression. In this study, we examined the expression of circ_0000199 in circulating exosomes from patients with OSCC and its role in the evaluation of relapse and prognosis. Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was performed to assess circ_0000199 expression in circulating exosomes from 108 patients with OSCC and 50 healthy people. Gain- and loss-functional experiments were performed to assess the role of circ_0000199 on cell proliferation and apoptosis in OSCC cells. Our results showed that the high level of circ_0000199 in circulating exosomes was significantly associated with betel quid chewing, tumor size, lymphatic metastasis, and TNM stage in patients with OSCC. In addition, the patients with high exosomal circ_0000199 had higher tumor recurrence rate and higher mortality rate than the patients with low exosomal circ_0000199. Overexpression of circ_0000199 promoted, while knockdown of circ_0000199 inhibited OSCC cell growth. Bioinformatics analysis predicted that circ_0000199 interacted with miR-145-5p and miR-29b-3p simultaneously, which were involved in multiple tumor-related signaling pathways. In conclusion, upregulation of circ_0000199 in circulating exosomes from patients with OSCC is positively associated with poor survival outcome. Circulating exosomal circ_0000199 can be used as a biomarker and potential therapeutic target for OSCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
hsa_circ_0072387 Suppresses Proliferation, Metastasis, and Glycolysis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Downregulating miR-503-5p.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021 Feb;36(1):84-94. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2019.3371. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021. PMID: 32302508
-
circRNA_0000140 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis by targeting miR-31 to inhibit Hippo signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Feb 10;11(2):112. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2273-y. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32041942 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of hsa_circ_0001971/miR-186 and hsa_circ_0001874/miR-296 signaling pathways promotes the proliferation of oral squamous carcinoma cells by synergistically activating SHP2/PLK1 signals.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 18;11(1):20561. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99488-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34663837 Free PMC article.
-
Underlying metastasis mechanism and clinical application of exosomal circular RNA in tumors (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Mar;58(3):289-297. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5179. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33650643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Profiling in Circulating Exosomes in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Aug 9;15(8):e43235. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43235. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37692575 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles in oral squamous cell carcinoma: current progress and future prospect.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 May 26;11:1149662. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1149662. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37304135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of circRNAs in Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-Associated Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;13(5):1173. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051173. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: Potential Biomarkers and Functions in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 14;9:881794. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.881794. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35775082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects for the clinical application of exosomal circular RNA in squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 12;14:1430684. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1430684. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38933443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting compensatory proliferation signals in oral cancer.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024 Jul-Aug;14(4):461-464. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2024.05.014. Epub 2024 Jun 7. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024. PMID: 38946920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

