Sodium-coupled glucose transport, the SLC5 family, and therapeutically relevant inhibitors: from molecular discovery to clinical application
- PMID: 32767111
- PMCID: PMC7462921
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-020-02433-x
Sodium-coupled glucose transport, the SLC5 family, and therapeutically relevant inhibitors: from molecular discovery to clinical application
Abstract
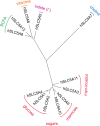
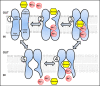
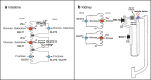
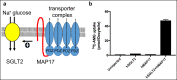
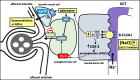
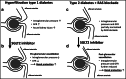
Sodium glucose transporters (SGLTs) belong to the mammalian solute carrier family SLC5. This family includes 12 different members in human that mediate the transport of sugars, vitamins, amino acids, or smaller organic ions such as choline. The SLC5 family belongs to the sodium symporter family (SSS), which encompasses transporters from all kingdoms of life. It furthermore shares similarity to the structural fold of the APC (amino acid-polyamine-organocation) transporter family. Three decades after the first molecular identification of the intestinal Na+-glucose cotransporter SGLT1 by expression cloning, many new discoveries have evolved, from mechanistic analysis to molecular genetics, structural biology, drug discovery, and clinical applications. All of these advances have greatly influenced physiology and medicine. While SGLT1 is essential for fast absorption of glucose and galactose in the intestine, the expression of SGLT2 is largely confined to the early part of the kidney proximal tubules, where it reabsorbs the bulk part of filtered glucose. SGLT2 has been successfully exploited by the pharmaceutical industry to develop effective new drugs for the treatment of diabetic patients. These SGLT2 inhibitors, termed gliflozins, also exhibit favorable nephroprotective effects and likely also cardioprotective effects. In addition, given the recent finding that SGLT2 is also expressed in tumors of pancreas and prostate and in glioblastoma, this opens the door to potential new therapeutic strategies for cancer treatment by specifically targeting SGLT2. Likewise, further discoveries related to the functional association of other SGLTs of the SLC5 family to human pathologies will open the door to potential new therapeutic strategies. We furthermore hope that the herein summarized information about the physiological roles of SGLTs and the therapeutic benefits of the gliflozins will be useful for our readers to better understand the molecular basis of the beneficial effects of these inhibitors, also in the context of the tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF), and the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). The detailed mechanisms underlying the clinical benefits of SGLT2 inhibition by gliflozins still warrant further investigation that may serve as a basis for future drug development.
Keywords: Cancer; Diabetes; Drug delivery; Gliflozins; Glucose transport; Molecular docking; Nephroprotective; Renin-angiotensin system; SGLT1; SGLT2; SGLT2 inhibitors; SLC5 family; Tubuloglomerular feedback.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporters: Functional properties and pharmaceutical potential.J Diabetes Investig. 2020 Jul;11(4):770-782. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13255. Epub 2020 Apr 16. J Diabetes Investig. 2020. PMID: 32196987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporters Family: Current Evidence, Clinical Applications and Perspectives.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 May 25;28(5):103. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2805103. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37258483 Review.
-
What does sodium-glucose co-transporter 1 inhibition add: Prospects for dual inhibition.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Apr;21 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):43-52. doi: 10.1111/dom.13630. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019. PMID: 31081587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active sugar transport in health and disease.J Intern Med. 2007 Jan;261(1):32-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2006.01746.x. J Intern Med. 2007. PMID: 17222166 Review.
-
Development of SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitors.Diabetologia. 2018 Oct;61(10):2079-2086. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4654-7. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 30132033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The results of SGLT-2 inhibitors use in kidney transplantation: 1-year experiences from two centers.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Nov;55(11):2989-2999. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03645-7. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37289399 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal trafficking of the glucose transporter GLUT1 requires sequential regulation by TXNIP and ubiquitin.iScience. 2023 Feb 6;26(3):106150. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106150. eCollection 2023 Mar 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36890792 Free PMC article.
-
The SGLT family-sodium-glucose transporters with roles beyond glucose and the kidney.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Mar;28(6):e18152. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18152. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38445802 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sodium Glucose Transporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT2Is)-TLRs Axis Modulates Diabetes.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023 Dec;81(4):599-613. doi: 10.1007/s12013-023-01164-x. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37658280 Review.
-
Systematic in silico discovery of novel solute carrier-like proteins from proteomes.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 28;17(7):e0271062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271062. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35901096 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

