Comparative effectiveness of pembrolizumab vs. nivolumab in patients with recurrent or advanced NSCLC
- PMID: 32753702
- PMCID: PMC7403144
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-70207-7
Comparative effectiveness of pembrolizumab vs. nivolumab in patients with recurrent or advanced NSCLC
Abstract
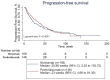
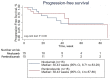
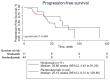
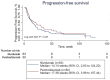
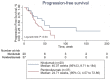
The efficacies of pembrolizumab and nivolumab have never been directly compared in a real-world study. Therefore, we sought to retrospectively evaluate the objective response rate (ORR) and the progression-free survival (PFS) of patients with recurrent or advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in a real-world setting. This study included patients with recurrent or advanced NSCLC diagnosed between September 1, 2015 and August 31, 2019, who were treated with programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) inhibitors at the Cancer Center of the Chinese People's Liberation Army. PFS was estimated for each treatment group using Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank tests. The multivariate analysis of PFS was performed with Cox proportional hazards regression models. A total of 255 patients with advanced or recurrent NSCLC treated with PD-1 inhibitors were identified. The ORR was significantly higher in the pembrolizumab group than in the nivolumab group, while PFS was not significantly different between the two groups. Subgroup analysis showed that the ORR was significantly higher for pembrolizumab than for nivolumab in patients in the first-line therapy subgroup and in those in the combination therapy as first-line therapy subgroup. Survival analysis of patients receiving combination therapy as second- or further-line therapy showed that nivolumab had better efficacy than pembrolizumab. However, the multivariate analysis revealed no significant difference in PFS between patients treated with pembrolizumab and those treated with nivolumab regardless of the subgroup. In our study, no significant difference in PFS was noted between patients treated with pembrolizumab and those treated with nivolumab in various clinical settings. This supports the current practice of choosing either pembrolizumab or nivolumab based on patient preferences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-world outcomes of anti-PD1 antibodies in platinum-refractory, PD-L1-positive recurrent and/or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, and its potential practical predictors: first report from Korean Cancer Study Group LU19-05.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Aug;147(8):2459-2469. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03527-4. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33523301
-
Profiling Preexisting Antibodies in Patients Treated With Anti-PD-1 Therapy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.JAMA Oncol. 2019 Mar 1;5(3):376-383. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.5860. JAMA Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30589930 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy Line and Associated Predictors of Response to PD-1/PD-L1-Inhibitor Monotherapy in Advanced Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Bi-centric Cohort Study.Target Oncol. 2019 Dec;14(6):707-717. doi: 10.1007/s11523-019-00679-9. Target Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31654203 Free PMC article.
-
Looking for the best immune-checkpoint inhibitor in pre-treated NSCLC patients: An indirect comparison between nivolumab, pembrolizumab and atezolizumab.Int J Cancer. 2018 Mar 15;142(6):1277-1284. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31136. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29080213 Review.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review.Clin Lung Cancer. 2017 Sep;18(5):444-459.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Clin Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28416123 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative efficacy of six programmed cell death Protein-1 inhibitors as first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter retrospective cohort study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 21;15:1390872. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1390872. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38835662 Free PMC article.
-
The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Influences the Resistance of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma to Monoclonal Antibodies via Its Effect on Energy Homeostasis and the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;13(23):5905. doi: 10.3390/cancers13235905. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of hematologic parameters in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving anti-PD-1 inhibitors.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 20;13:1003581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1003581. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36341410 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Influence of Subsequent Immunotherapy on Overall Survival in Patients with Unresectable Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer from the PACIFIC Study.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2021 Aug 12;95:100640. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2021.100640. eCollection 2021. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2021. PMID: 34484473 Free PMC article.
-
Photonanozyme-Kras-ribosome combination treatment of non-small cell lung cancer after COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 6;15:1420463. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1420463. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39308869 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

