RIPK protein kinase family: Atypical lives of typical kinases
- PMID: 32732131
- PMCID: PMC8286629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.06.014
RIPK protein kinase family: Atypical lives of typical kinases
Abstract
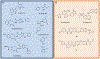
Receptor Interacting Protein Kinases (RIPKs) are a family of Ser/Thr/Tyr kinases whose functions, regulation and pathophysiologic roles have remained an enigma for a long time. In recent years, these proteins garnered significant interest due to their roles in regulating a variety of host defense functions including control of inflammatory gene expression, different forms of cell death, and cutaneous and intestinal barrier functions. In addition, there is accumulating evidence that while these kinases seemingly follow typical kinase blueprints, their functioning in cells can take forms that are atypical for protein kinases. Lastly, while these kinases generally belong to distinct areas of innate immune regulation, there are emerging overarching themes that may unify the functions of this kinase family. Our review seeks to discuss the biology of RIPKs, and how typical and atypical features of this family informs the activity of a rapidly growing repertoire of RIPK inhibitors.
Keywords: RIPK1; RIPK2; RIPK3; RIPK4; RIPK5; apoptosis; inflammation; kinase; necroptosis.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
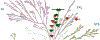
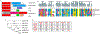
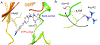
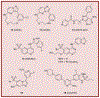
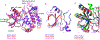
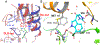
Similar articles
-
Tumor-intrinsic and immune modulatory roles of receptor-interacting protein kinases.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Apr;47(4):342-351. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.12.004. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 34998669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RIPK family: expression profile and prognostic value in lung adenocarcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Jul 30;14(14):5946-5958. doi: 10.18632/aging.204195. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35907206 Free PMC article.
-
Ripks and Neuroinflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):6771-6787. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03981-4. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38349514 Review.
-
Genomic and Transcriptional Analysis of the Necroptosis Pathway Elements RIPK and MLKL in Sea Cucumber, Holothuria leucospilota.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 3;15(10):1297. doi: 10.3390/genes15101297. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457421 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Biology Reveals the Uniqueness of the RIP Kinase Domain.J Immunol. 2016 May 15;196(10):4291-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502631. Epub 2016 Apr 4. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27045108 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
DSTYK inhibition increases the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity.J Exp Med. 2022 Dec 5;219(12):e20220726. doi: 10.1084/jem.20220726. Epub 2022 Sep 28. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 36169652 Free PMC article.
-
Necroptosis in CNS diseases: Focus on astrocytes.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jan 27;14:1016053. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1016053. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36778591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-intrinsic and immune modulatory roles of receptor-interacting protein kinases.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Apr;47(4):342-351. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.12.004. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 34998669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The involvement of RIPK4 in TNF-α-stimulated IL-6 and IL-8 production by melanoma cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Apr 24;150(4):209. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05732-3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38656555 Free PMC article.
-
The RIPK family: expression profile and prognostic value in lung adenocarcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Jul 30;14(14):5946-5958. doi: 10.18632/aging.204195. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35907206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stanger BZ, et al., RIP: a novel protein containing a death domain that interacts with Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death. Cell, 1995. 81(4): p. 513–23. - PubMed
-
- Kelliher MA, et al., The death domain kinase RIP mediates the TNF-induced NF-kappaB signal. Immunity, 1998. 8(3): p. 297–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

