Kidney Replacement Therapy in COVID-19 Induced Kidney Failure and Septic Shock: A Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy [PCRRT] Position on Emergency Preparedness With Resource Allocation
- PMID: 32719758
- PMCID: PMC7347905
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2020.00413
Kidney Replacement Therapy in COVID-19 Induced Kidney Failure and Septic Shock: A Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy [PCRRT] Position on Emergency Preparedness With Resource Allocation
Abstract
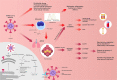
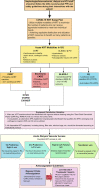
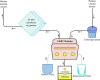
The recent worldwide pandemic of COVID-19 has had a detrimental worldwide impact on people of all ages. Although data from China and the United States indicate that pediatric cases often have a mild course and are less severe in comparison to adults, there have been several cases of kidney failure and multisystem inflammatory syndrome reported. As such, we believe that the world should be prepared if the severity of cases begins to further increase within the pediatric population. Therefore, we provide here a position paper centered on emergency preparation with resource allocation for critical COVID-19 cases within the pediatric population, specifically where renal conditions worsen due to the onset of AKI.
Keywords: COVID-19; acute kidney injury; extracorporeal therapy; kidney replacement therapy; pediatrics.
Copyright © 2020 Raina, Chakraborty, Sethi and Bunchman.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PCRRT-ICONIC critical care pediatric nephrology course: the global prevalence of COVID-19 and associated sequelae.Front Nephrol. 2022 Oct 5;2:1008629. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2022.1008629. eCollection 2022. Front Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 37675029 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating Shortages in Capacity to Deliver Continuous Kidney Replacement Therapy During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the United States.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Nov;76(5):696-709.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 32730812 Free PMC article.
-
PCRRT Expert Committee ICONIC Position Paper on Prescribing Kidney Replacement Therapy in Critically Sick Children With Acute Liver Failure.Front Pediatr. 2022 Feb 2;9:833205. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.833205. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35186830 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy.Contrib Nephrol. 2016;187:121-30. doi: 10.1159/000442370. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Contrib Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26881430 Review.
-
[COVID-19 and acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit].Nephrologe. 2021;16(1):20-25. doi: 10.1007/s11560-020-00471-1. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Nephrologe. 2021. PMID: 33362880 Free PMC article. Review. German.
Cited by
-
Dialysis resource allocation in critical care: the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the promise of big data analytics.Front Nephrol. 2023 Oct 26;3:1266967. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2023.1266967. eCollection 2023. Front Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37965069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute kidney injury in children with COVID-19: a retrospective study.BMC Nephrol. 2021 May 31;22(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02389-9. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34059010 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney disease and COVID-19 disease severity-systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2022 Feb;22(1):125-135. doi: 10.1007/s10238-021-00715-x. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Clin Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 33891214 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of extracorporeal blood purification techniques in critically ill patients before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Egypt.Acute Crit Care. 2024 Feb;39(1):70-77. doi: 10.4266/acc.2023.00654. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Acute Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 38303583 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the treatment of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19.Future Virol. 2022 Dec:10.2217/fvl-2022-0048. doi: 10.2217/fvl-2022-0048. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Future Virol. 2022. PMID: 36699562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zick M. Can COVID-19 Cause Sepsis? Explaining the Relationship Between the Coronavirus Disease and Sepsis. Global Sepsis Alliance. (2020). Available online at: https://www.global-sepsis-alliance.org/news/2020/3/4/can-covid-19-cause-...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

