Long-chain fatty acyl-CoA esters regulate metabolism via allosteric control of AMPK β1 isoforms
- PMID: 32719536
- PMCID: PMC7502547
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-020-0245-2
Long-chain fatty acyl-CoA esters regulate metabolism via allosteric control of AMPK β1 isoforms
Abstract
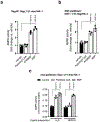
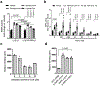
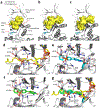
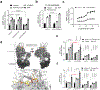
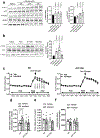
Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) play important roles in cellular energy metabolism, acting as both an important energy source and signalling molecules1. LCFA-CoA esters promote their own oxidation by acting as allosteric inhibitors of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which reduces the production of malonyl-CoA and relieves inhibition of carnitine palmitoyl-transferase 1, thereby promoting LCFA-CoA transport into the mitochondria for β-oxidation2-6. Here we report a new level of regulation wherein LCFA-CoA esters per se allosterically activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) β1-containing isoforms to increase fatty acid oxidation through phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Activation of AMPK by LCFA-CoA esters requires the allosteric drug and metabolite site formed between the α-subunit kinase domain and the β-subunit. β1 subunit mutations that inhibit AMPK activation by the small-molecule activator A769662, which binds to the allosteric drug and metabolite site, also inhibit activation by LCFA-CoAs. Thus, LCFA-CoA metabolites act as direct endogenous AMPK β1-selective activators and promote LCFA oxidation.
Figures
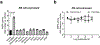
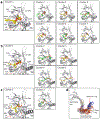
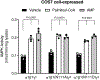
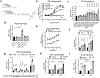
Similar articles
-
Preservation of Acyl Coenzyme A Attenuates Pathological and Metabolic Cardiac Remodeling Through Selective Lipid Trafficking.Circulation. 2019 Jun 11;139(24):2765-2777. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.039610. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 30909726 Free PMC article.
-
Malonyl-CoA, fuel sensing, and insulin resistance.Am J Physiol. 1999 Jan;276(1):E1-E18. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1999.276.1.E1. Am J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 9886945 Review.
-
Thienopyridone drugs are selective activators of AMP-activated protein kinase beta1-containing complexes.Chem Biol. 2008 Nov 24;15(11):1220-30. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.10.005. Chem Biol. 2008. PMID: 19022182
-
Probing the enzyme kinetics, allosteric modulation and activation of α1- and α2-subunit-containing AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) heterotrimeric complexes by pharmacological and physiological activators.Biochem J. 2016 Mar 1;473(5):581-92. doi: 10.1042/BJ20151051. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 26635351 Free PMC article.
-
Malonyl CoA, long chain fatty acyl CoA and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 1998;9(2-4):295-308. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp.1998.9.2-4.295. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 10212840 Review.
Cited by
-
The phosphorylation of AMPKβ1 is critical for increasing autophagy and maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis in response to fatty acids.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Nov 29;119(48):e2119824119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2119824119. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36409897 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Adipocytokine Pathway-Related Genes in Epilepsy and Its Effect on the Peripheral Immune Landscape.Brain Sci. 2022 Aug 30;12(9):1156. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12091156. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36138892 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into activation and function of the AMPK.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Apr;24(4):255-272. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00547-x. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36316383 Review.
-
AMPK role in epilepsy: a promising therapeutic target?J Neurol. 2024 Feb;271(2):748-771. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-12062-w. Epub 2023 Nov 27. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38010498 Review.
-
Characterization of the "gut microbiota-immunity axis" and microbial lipid metabolites in atrophic and potential celiac disease.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 30;13:886008. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.886008. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36246269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bortz WM & Lynen F THE INHIBITION OF ACETYL COA CARBOXYLASE BY LONG CHAIN ACYL COA DERIVATIVES. Biochem Z 337, 505–509 (1963). - PubMed
-
- McGarry JD & Foster DW In support of the roles of malonyl-CoA and carnitine acyltransferase I in the regulation of hepatic fatty acid oxidation and ketogenesis. J Biol Chem 254, 8163–8168 (1979). - PubMed
-
- McGarry JD, Takabayashi Y & Foster DW The role of malonyl-coa in the coordination of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 253, 8294–8300 (1978). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

