Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: new mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects
- PMID: 32680511
- PMCID: PMC7367382
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01234-1
Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: new mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects
Abstract
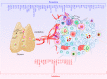
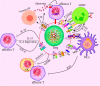
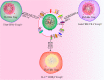
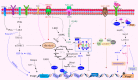
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) characterized by the expression of the master transcription factor forkhead box protein p3 (Foxp3) suppress anticancer immunity, thereby hindering protective immunosurveillance of tumours and hampering effective antitumour immune responses in tumour-bearing hosts, constitute a current research hotspot in the field. However, Tregs are also essential for the maintenance of the immune tolerance of the body and share many molecular signalling pathways with conventional T cells, including cytotoxic T cells, the primary mediators of tumour immunity. Hence, the inability to specifically target and neutralize Tregs in the tumour microenvironment without globally compromising self-tolerance poses a significant challenge. Here, we review recent advances in characterizing tumour-infiltrating Tregs with a focus on the functional roles of costimulatory and inhibitory receptors in Tregs, evaluate their potential as clinical targets, and systematically summarize their roles in potential treatment strategies. Also, we propose modalities to integrate our increasing knowledge on Tregs phenotype and function for the rational design of checkpoint inhibitor-based combination therapies. Finally, we propose possible treatment strategies that can be used to develop Treg-targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of costimulatory and inhibitory receptors in FoxP3+ regulatory T cells within the tumor microenvironment: Implications for combination immunotherapy approaches.Adv Cancer Res. 2019;144:193-261. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2019.05.001. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Adv Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31349899 Review.
-
Metabolic profiles of regulatory T cells in the tumour microenvironment.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Sep;70(9):2417-2427. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02881-z. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33576875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in cancer: Prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Cancer Lett. 2020 Oct 10;490:174-185. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.07.022. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32721551 Review.
-
Immunometabolic Checkpoints of Treg Dynamics: Adaptation to Microenvironmental Opportunities and Challenges.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 27;10:1889. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01889. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31507585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reprogramming the Tumor Microenvironment to Improve Immunotherapy: Emerging Strategies and Combination Therapies.Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2019 Jan;39:165-174. doi: 10.1200/EDBK_237987. Epub 2019 May 17. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2019. PMID: 31099649 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amphiregulin promotes activated regulatory T cell-suppressive function via the AREG/EGFR pathway in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Head Face Med. 2024 Oct 26;20(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13005-024-00466-6. Head Face Med. 2024. PMID: 39456084 Free PMC article.
-
CAR NK Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma: Potential & Prospects.Cells. 2023 Nov 30;12(23):2750. doi: 10.3390/cells12232750. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on anti-ovarian cancer mechanism of miRNA regulating tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1050917. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1050917. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAFAH1B3 Expression Is Correlated With Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation and Immune Infiltration.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 25;11:591545. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.591545. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33732641 Free PMC article.
-
The Combination of Bioavailable Concentrations of Curcumin and Resveratrol Shapes Immune Responses While Retaining the Ability to Reduce Cancer Cell Survival.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 23;25(1):232. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010232. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Mikami N, Wing JB, Tanaka A, Ichiyama K, Ohkura N. Regulatory T cells and human disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 2020;38:541–66. - PubMed
-
- Toker A, Ohashi PS. Expression of costimulatory and inhibitory receptors in FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells within the tumor microenvironment: implications for combination immunotherapy approaches. Adv Cancer Res. 2019;144:193–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

