Bi- and Tri-Specific T Cell Engager-Armed Oncolytic Viruses: Next-Generation Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 32664210
- PMCID: PMC7400484
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8070204
Bi- and Tri-Specific T Cell Engager-Armed Oncolytic Viruses: Next-Generation Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
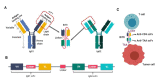
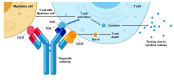
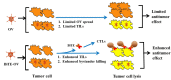
Oncolytic viruses (OVs) are potent anti-cancer biologics with a bright future, having substantial evidence of efficacy in patients with cancer. Bi- and tri-specific antibodies targeting tumor antigens and capable of activating T cell receptor signaling have also shown great promise in cancer immunotherapy. In a cutting-edge strategy, investigators have incorporated the two independent anti-cancer modalities, transforming them into bi- or tri-specific T cell engager (BiTE or TriTE)-armed OVs for targeted immunotherapy. Since 2014, multiple research teams have studied this combinatorial strategy, and it showed substantial efficacy in various tumor models. Here, we first provide a brief overview of the current status of oncolytic virotherapy and the use of multi-specific antibodies for cancer immunotherapy. We then summarize progress on BiTE and TriTE antibodies as a novel class of cancer therapeutics in preclinical and clinical studies, followed by a discussion of BiTE- or TriTE-armed OVs for cancer therapy in translational models. In addition, T cell receptor mimics (TCRm) have been developed into BiTEs and are expected to greatly expand the application of BiTEs and BiTE-armed OVs for the effective targeting of intracellular tumor antigens. Future applications of such innovative combination strategies are emerging as precision cancer immunotherapies.
Keywords: adenovirus; bispecific T cell engager; bispecific antibody; measles virus; oncolytic virus; trispecific T cell engager; trispecific antibody; tumor antigen-specific T cells; vaccinia virus.
Conflict of interest statement
X.-T.S. is the founder and CEO of Icell Kealex Therapeutics, a biotech company developing armed oncolytic viruses for cancer therapy. No other authors declare conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Revolutionizing cancer treatment: the power of bi- and tri-specific T-cell engagers in oncolytic virotherapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 22;15:1343378. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343378. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38464532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solid Tumor Immunotherapy with T Cell Engager-Armed Oncolytic Viruses.Macromol Biosci. 2018 Jan;18(1). doi: 10.1002/mabi.201700187. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Macromol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 28902983 Review.
-
Oncolytic viruses encoding bispecific T cell engagers: a blueprint for emerging immunovirotherapies.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Apr 16;14(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01075-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33863363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanobody-based trispecific T cell engager (Nb-TriTE) enhances therapeutic efficacy by overcoming tumor-mediated immunosuppression.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Nov 29;16(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01507-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38031188 Free PMC article.
-
Bi- and tri-valent T cell engagers deplete tumour-associated macrophages in cancer patient samples.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Nov 21;7(1):320. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0807-6. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31753017 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
AVL-armed oncolytic vaccinia virus promotes viral replication and boosts antitumor immunity via increasing ROS levels in pancreatic cancer.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Sep 17;32(4):200878. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200878. eCollection 2024 Dec 19. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39431173 Free PMC article.
-
Immunovirotherapy: The role of antibody based therapeutics combination with oncolytic viruses.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 13;13:1012806. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1012806. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncolytic Virus Engineering and Utilizations: Cancer Immunotherapy Perspective.Viruses. 2023 Jul 28;15(8):1645. doi: 10.3390/v15081645. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37631987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Immunotherapy Approaches for Treating Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 20;24(18):14347. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814347. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in oncolytic virus therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 26;13:1172292. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1172292. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37182136 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

