Single-Cell RNA Expression Profiling of ACE2, the Receptor of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32663409
- PMCID: PMC7462411
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202001-0179LE
Single-Cell RNA Expression Profiling of ACE2, the Receptor of SARS-CoV-2
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Single-Cell RNA Expression Profiling of ACE2, the Receptor of SARS-CoV-2.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Mar 15;203(6):782. doi: 10.1164/rccm.v203erratum4. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33719934 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Figures
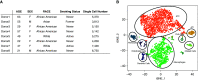
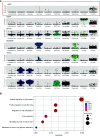
Similar articles
-
Expression of ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor, and TMPRSS2 in Prostate Epithelial Cells.Eur Urol. 2020 Aug;78(2):296-298. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.04.065. Epub 2020 May 6. Eur Urol. 2020. PMID: 32418620 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Co-Expression of Mitochondrial Genes and ACE2 in Cornea Involved in COVID-19.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Oct 1;61(12):13. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.12.13. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 33049061 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Pattern of the SARS-CoV-2 Entry Genes ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in the Respiratory Tract.Viruses. 2020 Oct 16;12(10):1174. doi: 10.3390/v12101174. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33081421 Free PMC article.
-
The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection.Eur J Intern Med. 2020 Jun;76:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Eur J Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32336612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 and the possible connection to ERs, ACE2, and RAGE: Focus on susceptibility factors.FASEB J. 2020 Nov;34(11):14103-14119. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001394RR. Epub 2020 Sep 23. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32965736 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Implications of cardiac markers in risk-stratification and management for COVID-19 patients.Crit Care. 2021 Apr 26;25(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03555-z. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33902676 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective: Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severity - plausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2 and thrombosis.J Intern Med. 2021 Jan;289(1):97-115. doi: 10.1111/joim.13149. Epub 2020 Jul 22. J Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 32613681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An ACE2 decoy can be administered by inhalation and potently targets omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2.EMBO Mol Med. 2022 Nov 8;14(11):e16109. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202216109. Epub 2022 Sep 23. EMBO Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36094679 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses in Covid-19 and Immunotherapeutic Approaches.Immunotargets Ther. 2021 Mar 9;10:63-85. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S280706. eCollection 2021. Immunotargets Ther. 2021. PMID: 33728277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe COVID-19 and aging: are monocytes the key?Geroscience. 2020 Aug;42(4):1051-1061. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00213-0. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Geroscience. 2020. PMID: 32556942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in China. medRxiv. 2020 Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.06.20020974v1. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report-89. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

