Hyponastic Leaves 1 protects pri-miRNAs from nuclear exosome attack
- PMID: 32636270
- PMCID: PMC7382309
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2007203117
Hyponastic Leaves 1 protects pri-miRNAs from nuclear exosome attack
Abstract
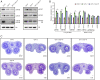
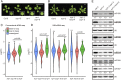
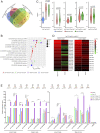
Biogenesis of plant microRNAs (miRNAs) takes place in nuclear dicing bodies (D-bodies), where the ribonulease III-type enzyme Dicer-like 1 (DCL1) processes primary transcripts of miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) into miRNA/miRNA* (*, passenger strand) duplexes from either base-to-loop or loop-to-base directions. Hyponastic Leaves 1 (HYL1), a double-stranded RNA-binding protein, is crucial for efficient and accurate processing. However, whether HYL1 has additional function remains unknown. Here, we report that HYL1 plays a noncanonical role in protecting pri-miRNAs from nuclear exosome attack in addition to ensuring processing. Loss of functions in SOP1 or HEN2, two cofactors of the nucleoplasmic exosome, significantly suppressed the morphological phenotypes of hyl1-2 Remarkably, mature miRNAs generated from loop-to-base processing were partially but preferentially restored in the hyl1 sop1 and hyl1 hen2 double mutants. Accordingly, loop-to-base-processed pri-miRNAs accumulated to higher levels in double mutants. In addition, dysfunction of HEN2, but not of SOP1, in hyl1-2 resulted in overaccumulation of many base-to-loop-processed pri-miRNAs, with most of their respective miRNAs unaffected. In summary, our findings reveal an antagonistic action of exosome in pri-miRNA biogenesis and uncover dual roles of HYL1 in stabilizing and processing of pri-miRNAs.
Keywords: HEN2; HYL1; SOP1; exosome; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The interaction between DCL1 and HYL1 is important for efficient and precise processing of pri-miRNA in plant microRNA biogenesis.RNA. 2006 Feb;12(2):206-12. doi: 10.1261/rna.2146906. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16428603 Free PMC article.
-
Complementation of HYPONASTIC LEAVES1 by double-strand RNA-binding domains of DICER-LIKE1 in nuclear dicing bodies.Plant Physiol. 2013 Sep;163(1):108-17. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.219071. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23886622 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-microRNA processing activity in nuclear extracts from Arabidopsis suspension cells.J Plant Res. 2017 Jan;130(1):75-82. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0874-4. Epub 2016 Nov 24. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27885505
-
HYL1's multiverse: A journey through miRNA biogenesis and beyond canonical and non-canonical functions of HYL1.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024 Aug;80:102546. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2024.102546. Epub 2024 May 7. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38718678 Review.
-
Keeping up with the miRNAs: current paradigms of the biogenesis pathway.J Exp Bot. 2023 Apr 9;74(7):2213-2227. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac322. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 35959860 Review.
Cited by
-
An insight into microRNA biogenesis and its regulatory role in plant secondary metabolism.Plant Cell Rep. 2022 Aug;41(8):1651-1671. doi: 10.1007/s00299-022-02877-8. Epub 2022 May 17. Plant Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35579713 Review.
-
ARF3-Mediated Regulation of SPL in Early Anther Morphogenesis: Maintaining Precise Spatial Distribution and Expression Level.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 21;24(14):11740. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411740. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511499 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis AAR2, a conserved splicing factor in eukaryotes, acts in microRNA biogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 11;119(41):e2208415119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208415119. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36191209 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of MicroRNA Biogenesis and Stability Control in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 8;13:844149. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.844149. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35350301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA biogenesis and stabilization in plants.Fundam Res. 2023 Mar 17;3(5):707-717. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2023.02.023. eCollection 2023 Sep. Fundam Res. 2023. PMID: 38933298 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li S., Castillo-González C., Yu B., Zhang X., The functions of plant small RNAs in development and in stress responses. Plant J. 90, 654–670 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Vazquez F., Gasciolli V., Crété P., Vaucheret H., The nuclear dsRNA binding protein HYL1 is required for microRNA accumulation and plant development, but not posttranscriptional transgene silencing. Curr. Biol. 14, 346–351 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

