Evaluation of Next Generation Sequencing for Detecting HER2 Copy Number in Breast and Gastric Cancers
- PMID: 32621174
- PMCID: PMC7471150
- DOI: 10.1007/s12253-020-00844-w
Evaluation of Next Generation Sequencing for Detecting HER2 Copy Number in Breast and Gastric Cancers
Abstract
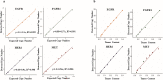
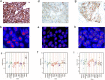
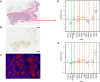
Amplicon-based next generation sequencing (NGS) approaches have been preferentially adopted by the clinical laboratories on the basis of a short turnaround time (TAT) and small DNA input needs. However, little work has been done to assess the amplicon-based NGS methods for copy number variation (CNV) detection in comparison with current standard methods like immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). The correlation between NGS based CNV detection and the later standard methods has remained unexplored. We developed an amplicon-based panel to detect human epidermal receptor growth factor (HER2) amplification in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumor tissue samples from 280 breast cancer and 50 gastric cancer patients. Assessment by IHC and FISH was conducted in parallel, and descriptive statistics were used to assess the concordance. The copy number detected by NGS was correlated with either the average HER2 copy number (signals/cell) (r = 0.844; p < 0.001) or the HER2/CEP17 ratio (r = 0.815; p < 0.001). We determined a cut-off value for NGS to categorize HER2 amplification status by using 151 HER2 non-amplified FFPE samples. In breast cancer patients, the cut-off value was 2.910, with 95.35%, 98.67% and 97.29% sensitivity, specificity and concordance, respectively. However, this cut-off value displayed low sensitivity in gastric cancer patients (64.71%), and the following macrodissection procedure was not effective for increasing sensitivity (57.14%). Evaluation of HER2 copy number with NGS in our study was comparable with IHC and FISH in breast cancer patients, but concordance in gastric cancer was only moderate. The greater discordance in gastric cancer may reflect the underlying biological mechanisms, and further study is warranted. NGS-based HER2 assessment may decrease the equivocal HER2 determinations in breast cancer patients assessed by FISH/IHC.
Keywords: Breast cancer; FISH/IHC; Gastric cancer; HER2 amplification; Next generation sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Lei Li, Wanchun Zang, Lianju Gao, Guanhua Rao, Yun Gao, Gang Cheng and Yang Yu were employee of Novogene Bioinformatics Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors. SJK has received consulting/advisory fees from Lilly Oncology, Astellas, Boston Biomedical and Foundation Medicine, Inc. SJK has stock/equity in TP Therapeutics and receives institutional research funding from Merck, Leap therapeutics, and Astellas Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 amplification detection by droplet digital polymerase chain reaction in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast and gastric cancer samples.J Cancer Res Ther. 2017;13(4):730-734. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_587_17. J Cancer Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28901323
-
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction detection of HER2 amplification in formalin fixed paraffin embedded breast and gastric carcinoma samples.Exp Mol Pathol. 2016 Apr;100(2):287-93. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.11.027. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Exp Mol Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26626802
-
HER2/ERBB2 copy number analysis by targeted next-generation sequencing in breast cancer.Am J Clin Pathol. 2024 May 2;161(5):436-442. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqad167. Am J Clin Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38104247
-
Computational methods for detecting copy number variations in cancer genome using next generation sequencing: principles and challenges.Oncotarget. 2013 Nov;4(11):1868-81. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1537. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 24240121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ISH-based HER2 diagnostics.Pathologe. 2021 Nov;42(Suppl 1):62-68. doi: 10.1007/s00292-020-00878-6. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Pathologe. 2021. PMID: 33346874 Review. English.
Cited by
-
MET Amplification in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)-A Consecutive Evaluation Using Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) in a Real-World Setting.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 7;13(19):5023. doi: 10.3390/cancers13195023. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638507 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of a putative HER2-associated expressed enhancer, Her2-Enhancer1, in breast cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 9;13(1):19516. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46460-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37945744 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiota between Captive and Wild Long-Tailed Gorals for Ex Situ Conservation.Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 12;12(7):1419. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071419. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065187 Free PMC article.
-
Positive predictive value of ERBB2 copy number gain by tissue or circulating tumor DNA next-generation sequencing across advanced cancers.Oncotarget. 2022 Feb 2;13:273-280. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28188. eCollection 2022. Oncotarget. 2022. PMID: 35126865 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Through DNA, mRNA, and Protein in Diverse Malignancies.JCO Precis Oncol. 2023 Jul;7:e2200604. doi: 10.1200/PO.22.00604. JCO Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37437231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rehm HL, Bale SJ, Bayrak-Toydemir P, Berg JS, Brown KK, Deignan JL, Friez MJ, Funke BH, Hegde MR, Lyon E, Working Group of the American College of Medical G, Genomics Laboratory Quality Assurance C ACMG clinical laboratory standards for next-generation sequencing. Genet Med. 2013;15(9):733–747. doi: 10.1038/gim.2013.92. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hamblin A, Wordsworth S, Fermont JM, Page S, Kaur K, Camps C, Kaisaki P, Gupta A, Talbot D, Middleton M, Henderson S, Cutts A, Vavoulis DV, Housby N, Tomlinson I, Taylor JC, Schuh A. Clinical applicability and cost of a 46-gene panel for genomic analysis of solid tumours: retrospective validation and prospective audit in the UK National Health Service. PLoS Med. 2017;14(2):e1002230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002230. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pfarr N, Penzel R, Endris V, Lier C, Flechtenmacher C, Volckmar AL, Kirchner M, Budczies J, Leichsenring J, Herpel E, Noske A, Weichert W, Schneeweiss A, Schirmacher P, Sinn HP, Stenzinger A. Targeted next-generation sequencing enables reliable detection of HER2 (ERBB2) status in breast cancer and provides ancillary information of clinical relevance. Gene Chromosome Cancer. 2017;56(4):255–265. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22431. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T, Shimojima K, Ondo Y, Imai K, Chong PF, Kira R, Amemiya M, Saito A, Okamoto N. Challenges in detecting genomic copy number aberrations using next-generation sequencing data and the eXome hidden Markov model: a clinical exome-first diagnostic approach. Hum Genome Var. 2016;3:16025. doi: 10.1038/hgv.2016.25. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

