LncRNA TDRG1 Promotes Proliferation, Invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation of Osteosarcoma Through PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway
- PMID: 32606946
- PMCID: PMC7304679
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S248964
LncRNA TDRG1 Promotes Proliferation, Invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation of Osteosarcoma Through PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the effect of long non-coding TDRG1 on proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
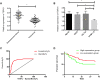
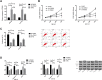
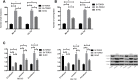
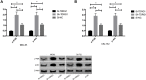
Materials and methods: Altogether 87 cases of osteosarcoma tissues and adjacent tissues were collected, and osteosarcoma cells and osteoblasts were purchased. The expression of LncRNA TDRG1 in tissues and cells was detected by RT-PCR. Si-NC, si-TDRG1, and Sh-TDRG1 were transfected into osteosarcoma cells. L740Y-P (activator of PI3K/AKT pathway) and LY294002 (inhibitor of PI3k/AKT pathway) were used to interfere with PI3k/Akt signaling pathway in osteosarcoma cells. qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of TDRG1 in osteosarcoma tissues and cells. WB was used to detect the expression of p-PI3K, p-AKT, N-cadherin, E-Cadherin, vimentin, Bax, Caspase-3, and Bcl-2 in cells. CCK-8, Transwell and cell scratch tests were used to detect cell proliferation, invasion and migration, and flow cytometry was used to detect cell apoptosis.
Results: TDRG1 was highly expressed in osteosarcoma, and the levels of p-PI3K and p-AKT were also up-regulated. Cell experiments showed that inhibiting the expression of TDRG1 could inhibit the proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT of osteosarcoma cells, promote the apoptosis of cells, and up-regulating the expression of TDRG1 could promote the proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT of osteosarcoma cells and inhibit the apoptosis of cells. The 740Y-P intervention could reverse the inhibition of Si-TDRG1 on osteosarcoma cell proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT and the promotion of cell apoptosis. LY294002 intervention could reverse the promotion of Sh-TDRG1 on osteosarcoma cell proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT and the inhibition of cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: TDRG1 is highly expressed in osteosarcoma tissue. Silencing the expression of osteosarcoma can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT of osteosarcoma cells by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, which may be a new target for diagnosis and treatment of osteosarcoma.
Keywords: LncRNA TDRG1; PI3K/AKT; migration; osteosarcoma cells; proliferation.
© 2020 Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-Chain Non-Coding SOX21-AS1 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells Through the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Nov 2;12:11005-11014. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S270464. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33173334 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of miR-202-5p silencing PIK3CA gene expression on proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer SiHa cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway activation.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Nov;476(11):4031-4044. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04211-4. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34244973
-
Knockdown of lncRNA TDRG1 Inhibits Tumorigenesis in Endometrial Carcinoma Through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Dec 11;12:10863-10872. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S228168. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31849490 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of MicroRNA/PI3K/AKT axis in osteosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 19;13:1219211. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1219211. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37404761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in regulatory T-cell development, stability, and function.J Leukoc Biol. 2018 Jan 22. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2MIR0817-349R. Online ahead of print. J Leukoc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29357116 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Chain Non-Coding SOX21-AS1 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells Through the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Nov 2;12:11005-11014. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S270464. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33173334 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the mechanisms of RECQL4-mediated cervical cancer progression through the PI3K/AKT pathway.Transl Oncol. 2024 Dec;50:102146. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102146. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39378549 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Dec 16;6(1):425. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00828-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34916492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of E-cadherin and N-cadherin in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Osteosarcoma: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Nov 27;15(11):e49521. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49521. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38156135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of glycolysis in osteosarcoma.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 17;13:950886. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.950886. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36059961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ogura K, Fujiwara T, Yasunaga H, et al. Development and external validation of nomograms predicting distant metastases and overall survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery for patients with nonmetastatic osteosarcoma: a multi-institutional study. Cancer. 2015;121(21):3844–3852. doi:10.1002/cncr.29575 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

