Gegen Qinlian Decoction Coordinately Regulates PPARγ and PPARα to Improve Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis in Diabetic Rats and Insulin Resistance 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
- PMID: 32595495
- PMCID: PMC7300300
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00811
Gegen Qinlian Decoction Coordinately Regulates PPARγ and PPARα to Improve Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis in Diabetic Rats and Insulin Resistance 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Abstract
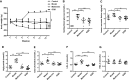
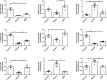
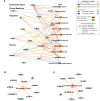
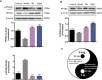
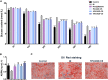
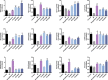
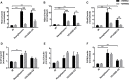
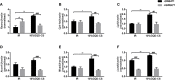
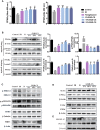
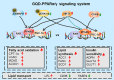
Gegen Qinlian Decoction (GQD), a well-documented traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) formula, was reported with convincing anti-diabetic effects in clinical practice. However, the precise antidiabetic mechanism of GQD remains unknown. In this study, the anti-hyperglycemic and/or lipid lowering effects of GQD were demonstrated in high-fat diet with a low dose of streptozotocin induced diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats and insulin resistance (IR)-3T3-L1 adipocytes. GQD treatment increased expression and activity levels of both PPARγ and PPARα in adipocytes, which transcriptionally affected an ensemble of glucose and lipid metabolic genes in vivo and in vitro. The results clearly indicated that GQD treatment intervened with multiple pathways controlled by concomitantly downstream effects of adipocytic PPARγ and PPARα, to influence two opposite lipid pathways: fatty acid oxidation and lipid synthesis. Antagonist GW9662 decreased the mRNA expression of Pparγ and target genes Adpn and Glut4 whereas GW6471 decreased the mRNA expression of Pparα and target genes Cpt-1α, Lpl, Mcad, Lcad, Acox1, etc. Nuclear location and activity experiments showed that more PPARγ and PPARα shuttled into nuclear to increase its binding activities with target genes. GQD decreased the phosphorylation level of ERK1/2 and/or CDK5 to elevate PPARγ and PPARα activities in IR-3T3-L1 adipocytes through post-translational modification. The increase in p-p38MAPK and SIRT1 under GQD treatment may be attributed to partially reduce PPARγ adipogenesis activity and/or activate PPARα activity. Compared with the rosiglitazone-treated group, GQD elevated Cpt-1α expression, decreased diabetic biomarker Fabp4 expression, which produced an encouraging lipid profile with triglyceride decrease partially from combined effects on upregulated adipocytic PPARγ and PPARα activities. These results suggested that GQD improved diabetes by intervening a diverse array of PPARγ and PPARα upstream and downstream signaling transduction cascades, which jointly optimized the expression of target gene profiles to promote fatty acid oxidation and accelerate glucose uptake and utilization than PPARγ full agonist rosiglitazone without stimulating PPARα activity. Thus, GQD showed anti-diabetic/or antihyperglycemic effects, partially through regulating adipocytic PPARα and PPARγ signaling systems to maintaining balanced glucose and lipid metabolisms. This study provides a new insight into the anti-diabetic effect of GQD as a PPARα/γ dual agonist to accelerate the clinical use.
Keywords: Gegen Qinlian Decoction; PPARα; PPARγ; glucose homeostasis; lipid metabolism.
Copyright © 2020 Tu, Zhu, Li, Xu, Luo, Jiang, Yan, Zhang and Chen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Gegen Qinlian decoction activates PPARγ to ameliorate adipocytic insulin resistance in diabetic SD rats and IR-3T3-L1 adipocytes].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Dec;42(23):4641-4648. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170928.003. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29376265 Chinese.
-
[Molecular mechanism of Gegen Qinlian Decoction in promoting differentiation of brown adipose tissue to improve glucose and lipid metabolism disorders in diabetic rats].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Sep;46(17):4462-4470. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210524.403. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34581051 Chinese.
-
Anti-diabetic activities of Gegen Qinlian Decoction in high-fat diet combined with streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Phytomedicine. 2013 Feb 15;20(3-4):221-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.11.002. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Phytomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23219338
-
Efficacy and safety of Gegen Qinlian decoction for normalizing hyperglycemia in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Complement Ther Med. 2017 Aug;33:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 26. Complement Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28735827 Review.
-
Constituents, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacology of Gegen-Qinlian Decoction.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 7;12:668418. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.668418. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34025427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ling-gui-zhu-gan promotes adipocytes browning via targeting the miR-27b/PRDM16 pathway in 3T3-L1 cells.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 14;15:1386794. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1386794. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39206264 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin and Gegen Qinlian Decoction boost islet α-cell proliferation of the STZ induced diabetic rats.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jul 20;22(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03674-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35858880 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Potential Mechanism of Alpinia officinarum Hance in Improving Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Feb 9;2023:4934711. doi: 10.1155/2023/4934711. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 36818229 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and Basis of Traditional Chinese Medicine Against Obesity: Prevention and Treatment Strategies.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 8;12:615895. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.615895. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33762940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of the Mechanism of the Control of Coccidiosis in Chickens Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking With the Addition of Modified Gegen Qinlian Decoction.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 17;9:849518. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.849518. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35372563 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

