Roles of Histone Deacetylases and Inhibitors in Anticancer Therapy
- PMID: 32585896
- PMCID: PMC7352721
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12061664
Roles of Histone Deacetylases and Inhibitors in Anticancer Therapy
Abstract
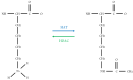
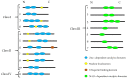
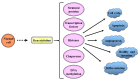
Histones are the main structural proteins of eukaryotic chromatin. Histone acetylation/ deacetylation are the epigenetic mechanisms of the regulation of gene expression and are catalyzed by histone acetyltransferases (HAT) and histone deacetylases (HDAC). These epigenetic alterations of DNA structure influence the action of transcription factors which can induce or repress gene transcription. The HATs catalyze acetylation and the events related to gene transcription and are also responsible for transporting newly synthesized histones from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. The activity of HDACs is mainly involved in silencing gene expression and according to their specialized functions are divided into classes I, II, III and IV. The disturbance of the expression and mutations of HDAC genes causes the aberrant transcription of key genes regulating important cancer pathways such as cell proliferation, cell-cycle regulation and apoptosis. In view of their role in cancer pathways, HDACs are considered promising therapeutic targets and the development of HDAC inhibitors is a hot topic in the search for new anticancer drugs. The present review will focus on HDACs I, II and IV, the best known inhibitors and potential alternative inhibitors derived from natural and synthetic products which can be used to influence HDAC activity and the development of new cancer therapies.
Keywords: cancer; chalcones; curcumin; histone acetyltransferase; histone deacetylase inhibitors; histone deacetylases; histones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in human cancer.Mol Oncol. 2007 Jun;1(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2007.01.001. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Mol Oncol. 2007. PMID: 19383284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of histone acetylation and deacetylation enzymes affects longevity, development, and fecundity in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum).Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020 Mar;103(3):e21614. doi: 10.1002/arch.21614. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31498475
-
The role dietary of bioactive compounds on the regulation of histone acetylases and deacetylases: a review.Gene. 2015 May 10;562(1):8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.02.045. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25701602 Review.
-
Using Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors to Analyze the Relevance of HDACs for Translation.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1510:77-91. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6527-4_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27761814
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: mechanisms and clinical significance in cancer: HDAC inhibitor-induced apoptosis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;615:261-98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-6554-5_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18437899 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and Function of StAR in Cancerous and Non-Cancerous Human and Mouse Breast Tissues: New Insights into Diagnosis and Treatment of Hormone-Sensitive Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 1;24(1):758. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010758. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614200 Free PMC article.
-
The role of viruses in cancer development versus cancer therapy: An oncological perspective.Cancer Med. 2023 May;12(10):11127-11148. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5694. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36880311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone regulator KAT2A acts as a potential biomarker related to tumor microenvironment and prognosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma.BMC Cancer. 2023 Oct 3;23(1):934. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11401-4. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37789275 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Multitarget-Directed Epi-Drugs in Blocking PI3K Oncogenic Signaling: A Polypharmacology Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 2;21(21):8198. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218198. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33147762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of HDAC10 as a candidate oncogene in clear cell renal carcinoma that facilitates tumor proliferation and metastasis.Diagn Pathol. 2024 Sep 5;19(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13000-024-01493-2. Diagn Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39237939 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

