ORP5 and ORP8: Sterol Sensors and Phospholipid Transfer Proteins at Membrane Contact Sites?
- PMID: 32570981
- PMCID: PMC7356933
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10060928
ORP5 and ORP8: Sterol Sensors and Phospholipid Transfer Proteins at Membrane Contact Sites?
Abstract
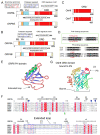
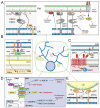
Oxysterol binding related proteins 5 and 8 (ORP5 and ORP8) are two close homologs of the larger oxysterol binding protein (OSBP) family of sterol sensors and lipid transfer proteins (LTP). Early studies indicated these transmembrane proteins, anchored to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), bound and sensed cholesterol and oxysterols. They were identified as important for diverse cellular functions including sterol homeostasis, vesicular trafficking, proliferation and migration. In addition, they were implicated in lipid-related diseases such as atherosclerosis and diabetes, but also cancer, although their mechanisms of action remained poorly understood. Then, alongside the increasing recognition that membrane contact sites (MCS) serve as hubs for non-vesicular lipid transfer, added to their structural similarity to other LTPs, came discoveries showing that ORP5 and 8 were in fact phospholipid transfer proteins that rather sense and exchange phosphatidylserine (PS) for phosphoinositides, including phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI(4)P) and potentially phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2). Evidence now points to their action at MCS between the ER and various organelles including the plasma membrane, lysosomes, mitochondria, and lipid droplets. Dissecting exactly how this unexpected phospholipid transfer function connects with sterol regulation in health or disease remains a challenge for future studies.
Keywords: OSBPL5; OSBPL8; PtdIns; PtdIns(4,5)P2; PtdIns4P; cortical endoplasmic reticulum; oxysterol binding protein like 5 and 8.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ORP5 and ORP8 bind phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-biphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P 2) and regulate its level at the plasma membrane.Nat Commun. 2017 Oct 2;8(1):757. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00861-5. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28970484 Free PMC article.
-
Oxysterol-binding proteins: sterol and phosphoinositide sensors coordinating transport, signaling and metabolism.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):529-38. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23830809 Review.
-
ORP5/ORP8 localize to endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contacts and are involved in mitochondrial function.EMBO Rep. 2016 Jun;17(6):800-10. doi: 10.15252/embr.201541108. Epub 2016 Apr 13. EMBO Rep. 2016. PMID: 27113756 Free PMC article.
-
INTRACELLULAR TRANSPORT. PI4P/phosphatidylserine countertransport at ORP5- and ORP8-mediated ER-plasma membrane contacts.Science. 2015 Jul 24;349(6246):428-32. doi: 10.1126/science.aab1370. Science. 2015. PMID: 26206935 Free PMC article.
-
The OSBP-related proteins (ORPs): global sterol sensors for co-ordination of cellular lipid metabolism, membrane trafficking and signalling processes?Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Jun;34(Pt 3):389-91. doi: 10.1042/BST0340389. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 16709169 Review.
Cited by
-
Sec22b regulates phagosome maturation by promoting ORP8-mediated lipid exchange at endoplasmic reticulum-phagosome contact sites.Commun Biol. 2023 Oct 4;6(1):1008. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05382-0. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37794132 Free PMC article.
-
ORP5 promotes migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Jul;28(4):395-407. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01357-6. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 37314629 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane: Overview and inextricable link with cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Apr;27(7):906-919. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17696. Epub 2023 Feb 27. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36852470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A fatty acid-ordered plasma membrane environment is critical for Ebola virus matrix protein assembly and budding.J Lipid Res. 2024 Nov;65(11):100663. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100663. Epub 2024 Oct 5. J Lipid Res. 2024. PMID: 39369791 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of Lipid Droplets with the Intracellular Transport Machinery.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 9;22(5):2776. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052776. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33803444 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- A Kandutsch A., Shown E.P. Assay of oxysterol-binding protein in a mouse fibroblast, cell-free system. Dissociation constant and other properties of the system. J. Boil. Chem. 1981;256:13068–13073. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

