Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 8 and 19 Regulate Host Cell Metabolism during Dengue Virus Serotype 2 Infection
- PMID: 32560467
- PMCID: PMC7354599
- DOI: 10.3390/v12060654
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 8 and 19 Regulate Host Cell Metabolism during Dengue Virus Serotype 2 Infection
Abstract
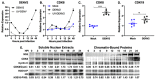
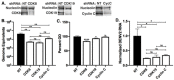
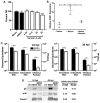
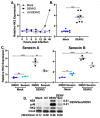
Dengue virus infection is associated with the upregulation of metabolic pathways within infected cells. This effect is common to infection by a broad array of viruses. These metabolic changes, including increased glucose metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation and autophagy, support the demands of viral genome replication and infectious particle formation. The mechanisms by which these changes occur are known to be, in part, directed by viral nonstructural proteins that contact and control cellular structures and metabolic enzymes. We investigated the roles of host proteins with overarching control of metabolic processes, the transcriptional regulators, cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8) and its paralog, CDK19, as mediators of virally induced metabolic changes. Here, we show that expression of CDK8, but not CDK19, is increased during dengue virus infection in Huh7 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells, although both are required for efficient viral replication. Chemical inhibition of CDK8 and CDK19 with Senexin A during infection blocks virus-induced expression of select metabolic and autophagic genes, hexokinase 2 (HK2) and microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3), and reduces viral genome replication and infectious particle production. The results further define the dependence of virus replication on increased metabolic capacity in target cells and identify CDK8 and CDK19 as master regulators of key metabolic genes. The common inhibition of CDK8 and CDK19 offers a host-directed therapeutic intervention that is unlikely to be overcome by viral evolution.
Keywords: CDK19; CDK8; LC3; Senexin; dengue virus; hexokinase; transcription; viral replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
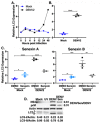
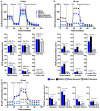
Similar articles
-
Regulation of autophagy, glucose uptake, and glycolysis under dengue virus infection.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020 Nov;36(11):911-919. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12271. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32783363
-
CDK8 Kinase Activity Promotes Glycolysis.Cell Rep. 2017 Nov 7;21(6):1495-1506. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.058. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 29117556 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Toxicity Reported for CDK8/19 Inhibitors CCT251921 and MSC2530818 Is Not Due to Target Inhibition.Cells. 2019 Nov 9;8(11):1413. doi: 10.3390/cells8111413. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31717492 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Development of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 8 Inhibitors.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(32):5429-5443. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190402110528. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 30947649 Review.
-
Expression of CDK8 and CDK8-interacting Genes as Potential Biomarkers in Breast Cancer.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15(8):739-49. doi: 10.2174/156800961508151001105814. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 26452386 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling tRNA fragments in DENV pathogenesis: Insights from RNA sequencing.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 7;14(1):18357. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69391-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39112524 Free PMC article.
-
CDK8 and CDK19: positive regulators of signal-induced transcription and negative regulators of Mediator complex proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Aug 11;51(14):7288-7313. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad538. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37378433 Free PMC article.
-
Exploitation of the Mediator complex by viruses.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Apr 21;18(4):e1010422. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010422. eCollection 2022 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35446926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dengue virus pathogenesis and host molecular machineries.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Apr 22;31(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01030-9. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38649998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple receptor tyrosine kinases regulate dengue infection of hepatocytes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Mar 22;14:1264525. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1264525. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38585651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Dengue and Severe Dengue. [(accessed on 20 January 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dengue-and-severe-dengue.
-
- World Health Organization. Pan American Health Organization Epidemiological Update: Dengue. [(accessed on 13 November 2019)]; Available online: http://www.paho.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

