Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Entry: Current and Future Opportunities
- PMID: 32539378
- PMCID: PMC7315836
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00502
Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Entry: Current and Future Opportunities
Abstract
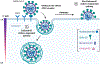
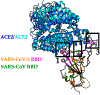
Recently, a novel coronavirus initially designated 2019-nCoV but now termed SARS-CoV-2 has emerged and raised global concerns due to its virulence. SARS-CoV-2 is the etiological agent of "coronavirus disease 2019", abbreviated to COVID-19, which despite only being identified at the very end of 2019, has now been classified as a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO). At this time, no specific prophylactic or postexposure therapy for COVID-19 are currently available. Viral entry is the first step in the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle and is mediated by the trimeric spike protein. Being the first stage in infection, entry of SARS-CoV-2 into host cells is an extremely attractive therapeutic intervention point. Within this review, we highlight therapeutic intervention strategies for anti-SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and other coronaviruses and speculate upon future directions for SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitor designs.
Figures

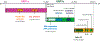
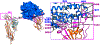
Similar articles
-
An Updated Review on Betacoronavirus Viral Entry Inhibitors: Learning from Past Discoveries to Advance COVID-19 Drug Discovery.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(7):571-596. doi: 10.2174/1568026621666210119111409. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33463470 Review.
-
Targeting the viral-entry facilitators of SARS-CoV-2 as a therapeutic strategy in COVID-19.J Med Virol. 2021 Sep;93(9):5260-5276. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27019. Epub 2021 May 3. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33851732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of S-protein RBD and hACE2 Interaction for Control of SARSCoV- 2 Infection (COVID-19).Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(6):689-703. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666201117111259. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33208074 Review.
-
Potential therapeutic approaches for the early entry of SARS-CoV-2 by interrupting the interaction between the spike protein on SARS-CoV-2 and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;192:114724. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114724. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34371003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Repurposed ACE2 Inhibitors: SARS-CoV-2 Entry Blockers of Covid-19.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021 Oct 8;379(6):40. doi: 10.1007/s41061-021-00353-7. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021. PMID: 34623536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coronavirus-Induced Host Cubic Membranes and Lipid-Related Antiviral Therapies: A Focus on Bioactive Plasmalogens.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 12;9:630242. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.630242. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33791293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting protein-protein interaction interfaces in COVID-19 drug discovery.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:2246-2255. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.003. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33936565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand-based discovery of coronavirus main protease inhibitors using MACAW molecular embeddings.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):24-35. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2132486. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36305272 Free PMC article.
-
Preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection using Fv-antibodies targeting the proprotein convertase (PPC) cleavage site.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Aug 26;15(11):3704-10. doi: 10.1039/d4md00552j. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39290379
-
Can polyoxometalates (POMs) prevent of coronavirus 2019-nCoV cell entry? Interaction of POMs with TMPRSS2 and spike receptor domain complexed with ACE2 (ACE2-RBD): Virtual screening approaches.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;29:100902. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.100902. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35284620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tong TR Therapies for coronaviruses. Part I of II – viral entry inhibitors. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat 2009, 19, 357–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

