Broad-Spectrum Host-Based Antivirals Targeting the Interferon and Lipogenesis Pathways as Potential Treatment Options for the Pandemic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- PMID: 32532085
- PMCID: PMC7354423
- DOI: 10.3390/v12060628
Broad-Spectrum Host-Based Antivirals Targeting the Interferon and Lipogenesis Pathways as Potential Treatment Options for the Pandemic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Abstract
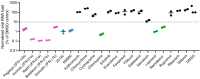
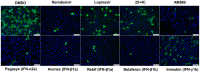
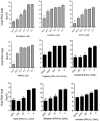
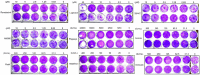
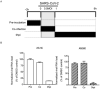
The ongoing Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) signals an urgent need for an expansion in treatment options. In this study, we investigated the anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities of 22 antiviral agents with known broad-spectrum antiviral activities against coronaviruses and/or other viruses. They were first evaluated in our primary screening in VeroE6 cells and then the most potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 antiviral agents were further evaluated using viral antigen expression, viral load reduction, and plaque reduction assays. In addition to remdesivir, lopinavir, and chloroquine, our primary screening additionally identified types I and II recombinant interferons, 25-hydroxycholesterol, and AM580 as the most potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents among the 22 antiviral agents. Betaferon (interferon-β1b) exhibited the most potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in viral antigen expression, viral load reduction, and plaque reduction assays among the recombinant interferons. The lipogenesis modulators 25-hydroxycholesterol and AM580 exhibited EC50 at low micromolar levels and selectivity indices of >10.0. Combinational use of these host-based antiviral agents with virus-based antivirals to target different processes of the SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle should be evaluated in animal models and/or clinical trials.
Keywords: 25-hydroxycholesterol; AM580; COVID-19; coronavirus; interferon; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
JFWC has received travel grants from Pfizer Corporation Hong Kong and Astellas Pharma Hong Kong Corporation Limited, and was an invited speaker for Gilead Sciences Hong Kong Limited and Luminex Corporation. The other authors declared no conflict of interests. The funding sources had no role in study design, data collection, analysis or interpretation or writing of the report. The corresponding authors had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiviral activities of type I interferons to SARS-CoV-2 infection.Antiviral Res. 2020 Jul;179:104811. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104811. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 32360182 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Activity of Type I, II, and III Interferons Counterbalances ACE2 Inducibility and Restricts SARS-CoV-2.mBio. 2020 Sep 10;11(5):e01928-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01928-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32913009 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of the FDA-approved drugs bexarotene, cetilistat, diiodohydroxyquinoline, and abiraterone as potential COVID-19 treatments with a robust two-tier screening system.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:104960. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104960. Epub 2020 May 28. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32473310 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into antiviral mechanisms of remdesivir, lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine affecting the new SARS-CoV-2.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110668. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110668. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32861965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remdesivir against COVID-19 and Other Viral Diseases.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020 Oct 14;34(1):e00162-20. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00162-20. Print 2020 Dec 16. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 33055231 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Co-administration of Favipiravir and the Remdesivir Metabolite GS-441524 Effectively Reduces SARS-CoV-2 Replication in the Lungs of the Syrian Hamster Model.mBio. 2021 Feb 22;13(1):e0304421. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03044-21. Epub 2022 Feb 1. mBio. 2021. PMID: 35100870 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the outcomes of treatment with INF-β 1-a (interferon beta-1a) and IFN-β 1-b (interferon beta-1b) among COVID-19 inpatients.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt B):108241. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108241. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34688151 Free PMC article.
-
The Interaction Between Pulmonary Fibrosis and COVID-19 and the Application of Related Anti-Fibrotic Drugs.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 5;12:805535. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.805535. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35069217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico structure-based discovery of a SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Apr 10;17(6):1555-1564. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.59191. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33907519 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of (interferon beta-1b, lopinavir/ritonavir and ribavirin) versus favipiravir in hospitalized patients with non-critical COVID-19: A cohort study.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 10;16(6):e0252984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252984. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34111191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan J.F., Kok K.H., Zhu Z., Chu H., To K.K., Yuan S., Yuen K.Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2020;9:221–236. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Situation Report – 95. [(accessed on 25 April 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
-
- Chan J.F., Yuan S., Kok K.H., To K.K., Chu H., Yang J., Xing F., Liu J., Yip C.C.Y., Poon R.W.S., et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020;395:514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

