Role of Small Intestine and Gut Microbiome in Plant-Based Oral Tolerance for Hemophilia
- PMID: 32508814
- PMCID: PMC7251037
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00844
Role of Small Intestine and Gut Microbiome in Plant-Based Oral Tolerance for Hemophilia
Abstract
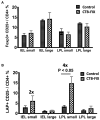
Fusion proteins, which consist of factor VIII or factor IX and the transmucosal carrier cholera toxin subunit B, expressed in chloroplasts and bioencapsulated within plant cells, initiate tolerogenic immune responses in the intestine when administered orally. This approach induces regulatory T cells (Treg), which suppress inhibitory antibody formation directed at hemophilia proteins induced by intravenous replacement therapy in hemophilia A and B mice. Further analyses of Treg CD4+ lymphocyte sub-populations in hemophilia B mice reveal a marked increase in the frequency of CD4+CD25-FoxP3-LAP+ T cells (but not of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ T cells) in the lamina propria of the small but not large intestine. The adoptive transfer of very small numbers of CD4+CD25-LAP+ Treg isolated from the spleen of tolerized mice was superior in suppression of antibodies directed against FIX when compared to CD4+CD25+ T cells. Thus, tolerance induction by oral delivery of antigens bioencapsulated in plant cells occurs via the unique immune system of the small intestine, and suppression of antibody formation is primarily carried out by induced latency-associated peptide (LAP) expressing Treg that likely migrate to the spleen. Tolerogenic antigen presentation in the small intestine requires partial enzymatic degradation of plant cell wall by commensal bacteria in order to release the antigen. Microbiome analysis of hemophilia B mice showed marked differences between small and large intestine. Remarkably, bacterial species known to produce a broad spectrum of enzymes involved in degradation of plant cell wall components were found in the small intestine, in particular in the duodenum. These were highly distinct from populations of cell wall degrading bacteria found in the large intestine. Therefore, FIX antigen presentation and Treg induction by the immune system of the small intestine relies on activity of a distinct microbiome that can potentially be augmented to further enhance this approach.
Keywords: factor IX; hemophilia; oral tolerance; regulatory T (Treg) cell; transgenic plant.
Copyright © 2020 Kumar, Wang, Avuthu, Bertolini, Terhorst, Guda, Daniell and Herzog.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Plant-based oral tolerance to hemophilia therapy employs a complex immune regulatory response including LAP+CD4+ T cells.Blood. 2015 Apr 9;125(15):2418-27. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-08-597070. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25700434 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Tolerance Induction in Hemophilia B Dogs Fed with Transplastomic Lettuce.Mol Ther. 2017 Feb 1;25(2):512-522. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.11.009. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28153098 Free PMC article.
-
B lymphocytes promote expansion of regulatory T cells in oral tolerance: powerful induction by antigen coupled to cholera toxin B subunit.J Immunol. 2008 Dec 15;181(12):8278-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8278. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19050244
-
In vivo induction of regulatory T cells for immune tolerance in hemophilia.Cell Immunol. 2016 Mar;301:18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Cell Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26454643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant cell-made protein antigens for induction of Oral tolerance.Biotechnol Adv. 2019 Nov 15;37(7):107413. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.06.012. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Biotechnol Adv. 2019. PMID: 31251968 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oral tolerance to prevent anti-drug antibody formation in protein replacement therapies.Cell Immunol. 2022 Dec;382:104641. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2022.104641. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Cell Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36402002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical development of plant-based oral immune modulatory therapy for haemophilia B.Plant Biotechnol J. 2021 Oct;19(10):1952-1966. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13608. Epub 2021 May 15. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33949086 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Designs of rAAVs Contribute to Pathological Changes in the Livers and Spleens of Mice.Adv Cell Gene Ther. 2022;2022:6807904. doi: 10.1155/2022/6807904. Epub 2022 Mar 20. Adv Cell Gene Ther. 2022. PMID: 36507314 Free PMC article.
-
Green giant-a tiny chloroplast genome with mighty power to produce high-value proteins: history and phylogeny.Plant Biotechnol J. 2021 Mar;19(3):430-447. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13556. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33484606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of anti-drug antibody formation against coagulation factor VIII by oral delivery of anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody in hemophilia A mice.Cell Immunol. 2023 Mar;385:104675. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2023.104675. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Cell Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36746071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pipe SW, Sabatino DE, Nugent DJ, Hooper WC, Soucie JM, Keith Hoots W, et al. . Executive summary of the NHLBI State of the Science (SOS) workshop: overview and next steps in generating a national blueprint for future research on factor VIII inhibitors. Haemophilia. (2019) 25:610–5. 10.1111/hae.13713 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

