Circular RNA HIPK3: A Key Circular RNA in a Variety of Human Cancers
- PMID: 32500032
- PMCID: PMC7242753
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00773
Circular RNA HIPK3: A Key Circular RNA in a Variety of Human Cancers
Abstract
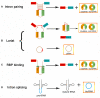
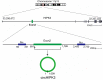
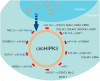
Circular RNAs (circRNAs), which act as initiators and promoters of various diseases, were thought to be mostly noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) in eukaryotes, until recent studies confirmed that some circRNAs have the function of encoding proteins. Accumulating research findings have proved that dysregulation of circRNAs is associated with the developmental process of multiple cancers. circHIPK3, an example of circRNA, is frequently expressed in many diseases, such as diabetes, age-related cataract, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, preeclampsia, osteoblasts, and retinal vascular dysfunction, leading to disease development and progression. In addition, circHIPK3 may also serve as a potential biomarker, to help us know more about the rules of occurrence and development of cancers. In recent studies, many circHIPK3-related cancers have been identified, including nasopharyngeal carcinoma, gallbladder cancer, lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, osteosarcoma, glioma, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer, gastric cancer, oral squamous cell carcinoma, and chronic myeloid leukemia. This review summarizes recent studies on the biological mechanisms of circHIPK3 and expounds the molecular mechanisms of circHIPK3 in these malignant tumors.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; circHIPK3; circular RNA; mRNA splicing; miRNA sponge.
Copyright © 2020 Wen, Liao, Liang, Chen, Zhang and Chu.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CircHIPK3: a promising cancer-related circular RNA.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Oct 15;12(10):6694-6704. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 33194066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular Noncoding RNA HIPK3 Mediates Retinal Vascular Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus.Circulation. 2017 Oct 24;136(17):1629-1642. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029004. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28860123
-
Comprehensive circular RNA expression profiles and the tumor-suppressive function of circHIPK3 in ovarian cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 Jul;112:8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.04.011. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31026505
-
Circular RNA HIPK3 regulates human lens epithelial cells proliferation and apoptosis by targeting the miR-193a/CRYAA axis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 18;503(4):2277-2285. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.149. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29959922
-
The circular RNA HIPK3 (circHIPK3) and its regulation in cancer progression: Review.Life Sci. 2020 Aug 1;254:117252. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117252. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31901445 Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging and quantification of human and viral circular RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 27;52(15):e70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae583. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39051561 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis, cellular effects, and biomarker value of circHIPK3.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 May 11;21(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01956-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33975598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging functions and significance of circCDYL in human disorders.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Dec 12;51(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08993-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 38085365 Review.
-
Mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitors: insights into the regulation of circular RNAS involved in cancer hallmarks.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jan 4;15(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06389-5. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38177102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological functions of circRNAs and their advance on skeletal muscle development in bovine.3 Biotech. 2023 May;13(5):133. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03558-3. Epub 2023 Apr 21. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37096117 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

