A framework to build similarity-based cohorts for personalized treatment advice - a standardized, but flexible workflow with the R package SimBaCo
- PMID: 32470056
- PMCID: PMC7259608
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233686
A framework to build similarity-based cohorts for personalized treatment advice - a standardized, but flexible workflow with the R package SimBaCo
Abstract
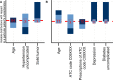
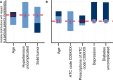
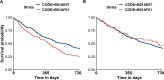
Along with increasing amounts of big data sources and increasing computer performance, real-world evidence from such sources likewise gains in importance. While this mostly applies to population averaged results from analyses based on the all available data, it is also possible to conduct so-called personalized analyses based on a data subset whose observations resemble a particular patient for whom a decision is to be made. Claims data from statutory health insurance companies could provide necessary information for such personalized analyses. To derive treatment recommendations from them for a particular patient in everyday care, an automated, reproducible and efficiently programmed workflow would be required. We introduce the R-package SimBaCo (Similarity-Based Cohort generation) offering a simple, but modular, and intuitive framework for this task. With the six built-in R-functions, this framework allows the user to create similarity cohorts tailored to the characteristics of particular patients. An exemplary workflow illustrates the distinct steps beginning with an initial cohort selection according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. A plotting function facilitates investigating a particular patient's characteristics relative to their distribution in a reference cohort, for example the initial cohort or the precision cohort after the data has been trimmed in accordance with chosen variables for similarity finding. Such precision cohorts allow any form of personalized analysis, for example personalized analyses of comparative effectiveness or customized prediction models developed from precision cohorts. In our exemplary workflow, we provide such a treatment comparison whereupon a treatment decision for a particular patient could be made. This is only one field of application where personalized results can directly support the process of clinical reasoning by leveraging information from individual patient data. With this modular package at hand, personalized studies can efficiently weight benefits and risks of treatment options of particular patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Personalized treatment options for chronic diseases using precision cohort analytics.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):1139. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-80967-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441956 Free PMC article.
-
Deriving Treatment Decision Support From Dutch Electronic Health Records by Exploring the Applicability of a Precision Cohort-Based Procedure for Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Precision Cohort Study.Online J Public Health Inform. 2024 May 1;16:e51092. doi: 10.2196/51092. Online J Public Health Inform. 2024. PMID: 38691393 Free PMC article.
-
netDx: Software for building interpretable patient classifiers by multi-'omic data integration using patient similarity networks.F1000Res. 2020 Oct 15;9:1239. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.26429.2. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 33628435 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and Interventions for Childhood Overweight [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2005 Jul. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2005 Jul. PMID: 20722132 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Tuberculosis.In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. PMID: 30212088 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Personalized treatment options for chronic diseases using precision cohort analytics.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):1139. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-80967-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441956 Free PMC article.
-
Using the Causal Inference Framework to Support Individualized Drug Treatment Decisions Based on Observational Healthcare Data.Clin Epidemiol. 2020 Nov 2;12:1223-1234. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S274466. eCollection 2020. Clin Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 33173350 Free PMC article.
-
Can Machine Learning from Real-World Data Support Drug Treatment Decisions? A Prediction Modeling Case for Direct Oral Anticoagulants.Med Decis Making. 2022 Jul;42(5):587-598. doi: 10.1177/0272989X211064604. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Med Decis Making. 2022. PMID: 34911402 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

