Propolis as A Potential Disease-Modifying Strategy in Parkinson's Disease: Cardioprotective and Neuroprotective Effects in the 6-OHDA Rat Model
- PMID: 32466610
- PMCID: PMC7352297
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12061551
Propolis as A Potential Disease-Modifying Strategy in Parkinson's Disease: Cardioprotective and Neuroprotective Effects in the 6-OHDA Rat Model
Abstract
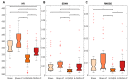
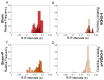
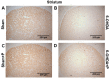
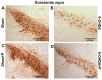
Patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) manifest nonmotor and motor symptoms. Autonomic cardiovascular dysregulation is a common nonmotor manifestation associated with increased morbimortality. Conventional clinical treatment alleviates motor signs but does not change disease progression and fails in handling nonmotor features. Nutrition is a key modifiable determinant of chronic disease. This study aimed to assess the effects of propolis on cardiological features, heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV) and on nigrostriatal dopaminergic damage, detected by tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunoreactivity, in the 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) rat model of PD. Male Wistar rats were injected bilaterally with 6-OHDA or saline into the striatum and were treated with propolis or water for 40 days. Autonomic function was assessed by time domain parameters (standard deviation of all normal-to-normal intervals (SDNN) and square root of the mean of the squared differences between adjacent normal RR intervals (RMSSD)) of HRV calculated from electrocardiogram recordings. Reductions in HR (p = 1.47×10-19), SDNN (p = 3.42×10-10) and RMSSD (p = 8.2×10-6) detected in parkinsonian rats were reverted by propolis. Propolis attenuated neuronal loss in the substantia nigra (p = 5.66×10-15) and reduced striatal fiber degeneration (p = 7.4×10-5) in 6-OHDA-injured rats, which also showed significant weight gain (p = 1.07×10-5) in comparison to 6-OHDA-lesioned counterparts. Propolis confers cardioprotection and neuroprotection in the 6-OHDA rat model of PD.
Keywords: 6-OHDA; Parkinson’s disease; propolis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
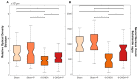
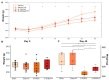
Similar articles
-
Dopaminergic neuroprotection and regeneration by neurturin assessed by using behavioral, biochemical and histochemical measurements in a model of progressive Parkinson's disease.Brain Res. 2002 Aug 30;947(2):271-83. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)02934-7. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12176170
-
Protective and therapeutic activity of honokiol in reversing motor deficits and neuronal degeneration in the mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Pharmacol Rep. 2018 Aug;70(4):668-676. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Pharmacol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29909247
-
Neuroprotective and neurorescue effect of black tea extract in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat model of Parkinson's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2006 May;22(2):421-34. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.12.008. Epub 2006 Feb 9. Neurobiol Dis. 2006. PMID: 16480889
-
The antioxidant drink effective microorganism-X (EM-X) pre-treatment attenuates the loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesion rat model of Parkinson's disease.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2004 May;56(5):649-54. doi: 10.1211/0022357023222. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15142343
-
Apitherapy for Parkinson's Disease: A Focus on the Effects of Propolis and Royal Jelly.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Oct 17;2020:1727142. doi: 10.1155/2020/1727142. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33123309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA-221 rescues the loss of dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Brain Behav. 2023 Mar;13(3):e2921. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2921. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 36795044 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden death in a rat model of Parkinson's disease.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021 Jun 14;76:e2974. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2974. eCollection 2021. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021. PMID: 34133483 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of cardiac β1-adrenergic and A1-adenosine receptors in severe arrhythmias related to Parkinson's disease.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2023 Jul 15;78:100243. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2023.100243. eCollection 2023. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2023. PMID: 37459671 Free PMC article.
-
Propolis Contra Pharmacological Interventions in Bees.Molecules. 2022 Aug 1;27(15):4914. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154914. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can Propolis Be a Useful Adjuvant in Brain and Neurological Disorders and Injuries? A Systematic Scoping Review of the Latest Experimental Evidence.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 15;9(9):1227. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091227. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572413 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saito Y., Nishio K., Ogawa Y., Kinumi T., Yoshida Y., Masuo Y., Niki E. Molecular mechanisms of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells: Involvement of hydrogen peroxide-dependent and -independent action. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007;42:675–685. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.12.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

