The Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Allies of HIV, HCV and SARS Viruses
- PMID: 32456011
- PMCID: PMC7291340
- DOI: 10.3390/v12050571
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Allies of HIV, HCV and SARS Viruses
Abstract
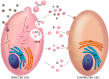
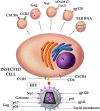
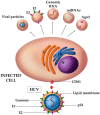
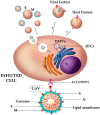
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are lipid bilayer-enclosed entities containing proteins and nucleic acids that mediate intercellular communication, in both physiological and pathological conditions. EVs resemble enveloped viruses in both structural and functional aspects. In full analogy with viral biogenesis, some of these vesicles are generated inside cells and, once released into the extracellular milieu, are called "exosomes". Others bud from the plasma membrane and are generally referred to as "microvesicles". In this review, we will discuss the state of the art of the current studies on the relationship between EVs and viruses and their involvement in three important viral infections caused by HIV, HCV and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) viruses. HIV and HCV are two well-known pathogens that hijack EVs content and release to create a suitable environment for viral infection. SARS viruses are a new entry in the world of EVs studies, but are equally important in this historical framework. A thorough knowledge of the involvement of the EVs in viral infections could be helpful for the development of new therapeutic strategies to counteract different pathogens.
Keywords: HCV; HIV; SARS viruses; coronaviruses; exosomes; extracellular vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis of Viral Infections in Humans.Viruses. 2020 Oct 21;12(10):1200. doi: 10.3390/v12101200. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33096825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections of the Nervous System.Viruses. 2020 Jun 28;12(7):700. doi: 10.3390/v12070700. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32605316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vehicles of intercellular communication: exosomes and HIV-1.J Gen Virol. 2019 Mar;100(3):350-366. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001193. Epub 2019 Jan 31. J Gen Virol. 2019. PMID: 30702421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles- crucial players in human pregnancy.Placenta. 2023 Sep 7;140:30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2023.07.006. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Placenta. 2023. PMID: 37531747 Review.
-
The complex role of extracellular vesicles in HIV infection.BMB Rep. 2023 Jun;56(6):335-340. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0073. BMB Rep. 2023. PMID: 37291055 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms underlying HIV-associated cognitive impairment and emerging therapies for its management.Nat Rev Neurol. 2023 Nov;19(11):668-687. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00879-y. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37816937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and Natural Viral Engineering in Cognition-Based Evolution.Commun Integr Biol. 2023 May 2;16(1):2196145. doi: 10.1080/19420889.2023.2196145. eCollection 2023. Commun Integr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37153718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: Roles in Human Viral Infections, Immune-Diagnostic, and Therapeutic Applications.Pathogens. 2020 Dec 17;9(12):1056. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9121056. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 33348699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA signature from extracellular vesicles of HCV/HIV co-infected individuals differs from HCV mono-infected.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Nov;101(11):1409-1420. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02367-8. Epub 2023 Sep 14. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37704856 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes Recovered From the Plasma of COVID-19 Patients Expose SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Derived Fragments and Contribute to the Adaptive Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 17;12:785941. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.785941. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35111156 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

