Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Antihypertensives (Angiotensin Receptor Blockers and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors) in Coronavirus Disease 2019
- PMID: 32376099
- PMCID: PMC7129862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.03.026
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Antihypertensives (Angiotensin Receptor Blockers and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors) in Coronavirus Disease 2019
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, is being defined as the worst pandemic disease of modern times. Several professional health organizations have published position papers stating that there is no evidence to change the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) in the management of elevated blood pressure in the context of avoiding or treating COVID-19 infection. In this article, we review the evidence on the relationship between the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and COVID-19 infection. In agreement with current guidelines, patients with hypertension should continue taking antihypertensive medications as prescribed without interruption. Because ACEIs and ARBs are also used to retard the progression of chronic kidney disease, we suggest that these recommendations also apply to the use of these agents in chronic kidney disease. No differences generally exist between ARBs and ACEIs in terms of efficacy in decreasing blood pressure and improving other outcomes, such as all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, myocardial infarction, heart failure, stroke, and end-stage renal disease. The ACEIs are associated with cough secondary to accumulation of bradykinin and angioedema, and withdrawal rates due to adverse events are lower with ARBs. Given their equal efficacy but fewer adverse events, ARBs could potentially be a more favorable treatment option in patients with COVID-19 at higher risk for severe forms of disease.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
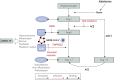
Comment in
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and the Resolution of Inflammation: In Support of Continuation of Prescribed Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers.Mayo Clin Proc. 2020 Jul;95(7):1552-1553. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.05.001. Epub 2020 May 21. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020. PMID: 32622456 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In reply-Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and the Resolution of Inflammation: In Support of Continuation of Prescribed Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers.Mayo Clin Proc. 2020 Jul;95(7):1553-1556. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 May 21. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020. PMID: 32622458 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Association of Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers With Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19.Mayo Clin Proc. 2020 Nov;95(11):2559-2561. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.09.010. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020. PMID: 33153642 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In reply- Association of Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers with Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19.Mayo Clin Proc. 2020 Nov;95(11):2561-2563. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.09.011. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020. PMID: 33153643 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
ACE2 (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2), COVID-19, and ACE Inhibitor and Ang II (Angiotensin II) Receptor Blocker Use During the Pandemic: The Pediatric Perspective.Hypertension. 2020 Jul;76(1):16-22. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15291. Epub 2020 May 5. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32367746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential harmful effects of discontinuing ACE-inhibitors and ARBs in COVID-19 patients.Elife. 2020 Apr 6;9:e57278. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57278. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32250244 Free PMC article.
-
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Patients with Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 23;382(17):1653-1659. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsr2005760. Epub 2020 Mar 30. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32227760 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Retrospective Study from 2 Centers in China on the Effects of Continued Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in Patients with Hypertension and COVID-19.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Sep 24;26:e926651. doi: 10.12659/MSM.926651. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32969367 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and renin-angiotensin system inhibition: role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) - Is there any scientific evidence for controversy?J Intern Med. 2020 Oct;288(4):410-421. doi: 10.1111/joim.13101. Epub 2020 Jun 8. J Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32459372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ACE2 Promotes the Synthesis of Pulmonary Surfactant to Improve AT II Cell Injury via SIRT1/eNOS Pathway.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Aug 21;2021:7710129. doi: 10.1155/2021/7710129. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9810987. doi: 10.1155/2023/9810987. PMID: 34471421 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Why is COVID-19 especially impacting the African American population?Ann Med. 2020 Nov;52(7):331-333. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1808695. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Ann Med. 2020. PMID: 32776788 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Renin-Angiotensin System, Hypertension, and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: a Review.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021 Mar 25;23(4):17. doi: 10.1007/s11906-021-01134-9. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021. PMID: 33768439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethnic Prevalence of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Deletion (D) Polymorphism and COVID-19 Risk: Rationale for Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors/Angiotensin Receptor Blockers.J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2021 Aug;8(4):973-980. doi: 10.1007/s40615-020-00853-0. Epub 2020 Sep 8. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2021. PMID: 32901433 Free PMC article.
-
Association between angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced cough and the risk of lung cancer: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 20;14:1267924. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1267924. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37799968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shah A., Kashyap R., Tosh P., Sampathkumar P., O’Horo J.C. Guide to understanding the 2019 novel coronavirus [published online February 28, 2020] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.02.003 Mayo Clin Proc. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahase E. Covid-19: WHO declares pandemic because of "alarming levels" of spread, severity, and inaction [published online March 12, 2020] https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m1036 BMJ. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lippi G., Sanchis-Gomar F., Henry B.M. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): the portrait of a perfect storm. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2020.03.157 Ann Transl Med. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report–62. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio... Published March 22, 2020. Accessed March 25, 2020.
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention [published online February 24, 2020] https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.2648 JAMA. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

