COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: A clinical-therapeutic staging proposal
- PMID: 32362390
- PMCID: PMC7118652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012
COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: A clinical-therapeutic staging proposal
Figures
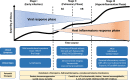
Comment in
-
COVID-19: Timing is Important.Eur J Intern Med. 2020 Jul;77:134-135. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.019. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Eur J Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32362362 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of heart transplant recipients during the 2019 coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China: A descriptive survey report.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020 May;39(5):412-417. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.008. Epub 2020 Mar 25. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32362392 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
ERCP during the pandemic of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China.Gastrointest Endosc. 2020 Aug;92(2):448-454. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.04.022. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020. PMID: 32305345 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infections in China: prevention, control and challenges.Intensive Care Med. 2020 Apr;46(4):591-593. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-05977-9. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Intensive Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32123989 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Large SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak Caused by Asymptomatic Traveler, China.Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Dec;26(12):3106. doi: 10.3201/eid2612.203437. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33219814 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19: Main therapeutic options.Tunis Med. 2020 Apr;98(4):299-303. Tunis Med. 2020. PMID: 32395792 Review. No abstract available.
-
Covid-19, chronicles of a forecasted pandemic.Tunis Med. 2020 Apr;98(4):295-298. Tunis Med. 2020. PMID: 32395791 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Impact of extracorporeal hemadsorption on mortality in critically ill COVID-19 patients in the intensive care unit.Int J Artif Organs. 2024 Oct;47(10):736-742. doi: 10.1177/03913988241269527. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Int J Artif Organs. 2024. PMID: 39268922 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive IDA and SWATH-DIA Lipidomics and Metabolomics dataset: SARS-CoV-2 case control study.Sci Data. 2024 Sep 12;11(1):998. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03822-y. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 39266559 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of methylprednisolone in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in high-risk patients: A retrospective study.SAGE Open Med. 2024 Sep 9;12:20503121241276683. doi: 10.1177/20503121241276683. eCollection 2024. SAGE Open Med. 2024. PMID: 39257516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic variants regulating the immune response improve the prediction of COVID-19 severity provided by clinical variables.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 5;14(1):20728. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71476-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39237611 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Study: Evaluating the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Inflammatory Markers in Hospitalized Patients.Infect Dis Rep. 2024 Aug 14;16(4):735-749. doi: 10.3390/idr16040056. Infect Dis Rep. 2024. PMID: 39195007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Novel coronavirus pneumonia emergency response epidemiology team The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China [in Chinese] Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41:145–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

