Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19
- PMID: 32356628
- PMCID: PMC7206932
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2008975
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19
Abstract
Background: There is concern about the potential of an increased risk related to medications that act on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in patients exposed to coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), because the viral receptor is angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).
Methods: We assessed the relation between previous treatment with ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-receptor blockers, beta-blockers, calcium-channel blockers, or thiazide diuretics and the likelihood of a positive or negative result on Covid-19 testing as well as the likelihood of severe illness (defined as intensive care, mechanical ventilation, or death) among patients who tested positive. Using Bayesian methods, we compared outcomes in patients who had been treated with these medications and in untreated patients, overall and in those with hypertension, after propensity-score matching for receipt of each medication class. A difference of at least 10 percentage points was prespecified as a substantial difference.
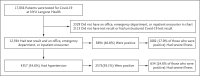
Results: Among 12,594 patients who were tested for Covid-19, a total of 5894 (46.8%) were positive; 1002 of these patients (17.0%) had severe illness. A history of hypertension was present in 4357 patients (34.6%), among whom 2573 (59.1%) had a positive test; 634 of these patients (24.6%) had severe illness. There was no association between any single medication class and an increased likelihood of a positive test. None of the medications examined was associated with a substantial increase in the risk of severe illness among patients who tested positive.
Conclusions: We found no substantial increase in the likelihood of a positive test for Covid-19 or in the risk of severe Covid-19 among patients who tested positive in association with five common classes of antihypertensive medications.
Copyright © 2020 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Inhibitors of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 18;382(25):2462-2464. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2012924. Epub 2020 May 1. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32356625 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
RAAS inhibitors do not increase the risk of COVID-19.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020 Jul;17(7):383. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-0401-0. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32444693 Free PMC article.
-
5 classes of antihypertensive drugs were not linked to positive COVID-19 test results or severe COVID-19.Ann Intern Med. 2020 Sep 15;173(6):JC35. doi: 10.7326/ACPJ202009150-035. Ann Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32926815
-
RAAS Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12;383(20):1990-1991. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2030446. Epub 2020 Oct 27. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33108102 No abstract available.
-
RAAS Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12;383(20):1991-1992. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2030446. Epub 2020 Oct 27. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33108103 No abstract available.
-
RAAS Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12;383(20):1992. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2030446. Epub 2020 Oct 27. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33108104 No abstract available.
-
RAAS Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12;383(20):1992-1993. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2030446. Epub 2020 Oct 27. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33108105 No abstract available.
-
RAAS Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12;383(20):1993. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2030446. Epub 2020 Oct 27. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33108106 No abstract available.
-
RAAS Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12;383(20):1993-1994. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2030446. Epub 2020 Oct 27. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 33108107 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Compliance of Antihypertensive Medication and Risk of Coronavirus Disease 2019: a Cohort Study Using Big Data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service.J Korean Med Sci. 2020 Jun 29;35(25):e232. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e232. J Korean Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32597045 Free PMC article.
-
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and the Risk of Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 18;382(25):2431-2440. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2006923. Epub 2020 May 1. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32356627 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and COVID-19 Infection in South Korea.Hypertension. 2020 Sep;76(3):742-749. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15464. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32654557
-
Considerations on the use of antihypertensive blockers of the renin-angiotensin system in adults and children in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic.Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2020;77(5):274-281. doi: 10.24875/BMHIM.20000158. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2020. PMID: 33064690 Review. English.
-
A review of chemical therapies for treating diabetic hypertension.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017 Jun;18(9):909-923. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2017.1328054. Epub 2017 May 16. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28480805 Review.
Cited by
-
Type 2 diabetes and susceptibility to COVID-19: a machine learning analysis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Oct 21;24(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01758-3. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 39434075 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and chronic kidney disease: a comprehensive review.J Bras Nefrol. 2021 Jul-Sep;43(3):383-399. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2020-0203. J Bras Nefrol. 2021. PMID: 33836039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Results of a hospitalization policy of asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic COVID-19-positive long-term care facility residents in the province of Salzburg-a report from the AGMT COVID-19 Registry.Geroscience. 2021 Aug;43(4):1877-1897. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00352-y. Epub 2021 Apr 10. Geroscience. 2021. PMID: 33837912 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease: from basic mechanisms to clinical perspectives.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020 Sep;17(9):543-558. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-0413-9. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32690910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proper Management of People with Obesity during the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Obes Metab Syndr. 2020 Jun 30;29(2):84-98. doi: 10.7570/jomes20056. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 32544885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferrario CM, Jessup J, Chappell MC, et al. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Circulation 2005;111:2605-2610. - PubMed
-
- Walters TE, Kalman JM, Patel SK, Mearns M, Velkoska E, Burrell LM. Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity and human atrial fibrillation: increased plasma angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity is associated with atrial fibrillation and more advanced left atrial structural remodelling. Europace 2017;19:1280-1287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
