Abnormalities of peripheral blood system in patients with COVID-19 in Wenzhou, China
- PMID: 32339487
- PMCID: PMC7194694
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.04.024
Abnormalities of peripheral blood system in patients with COVID-19 in Wenzhou, China
Abstract
Background: In December 2019, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was first found in Wuhan, China and soon was reported all around the world.
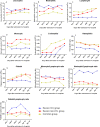
Methods: All confirmed cases with COVID-19 in Wenzhou from January 19 to February 20, 2020, were collected and analyzed. Of the 116 patients with COVID-19, 27 were diagnosed as severe cases. Among severe cases, 9 were treated in ICU. The data of blood routine examination were analyzed and compared among common patients (as common group), severe patients admitted to intensive care unit (as severe ICU group) and severe patients not admitted to ICU (as severe non-ICU group). The blood routine examination results were dynamically observed in the above groups after admission.
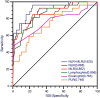
Results: Patients with COVID-19 have lower counts of leucocytes, lymphocytes, eosinophils, platelets, and hemoglobin, but have higher neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and monocyte-lymphocyte ratio (MLR), which were compared with controls (P < 0.001). In severe ICU group, patients have the lowest count of lymphocytes, but the highest neutrophil count and NLR among the above three groups (all P values < 0.05); NLR and MLR indicators were combined for diagnostic efficacy analysis of severe COVID-19, and its area under the curve reached 0.925. The odds ratio of the delay in days to the start of the increase of eosinophil count for predicting the outcome of patients with severe COVID-19 was 2.291 after age adjusted.
Conclusions: Patients with COVID-19 have abnormal peripheral blood routine examination results. Dynamic surveillance of peripheral blood system especially eosinophils is helpful in the prediction of severe COVID-19 cases.
Keywords: COVID-19; Eosinophils; Lymphocyte; Neutrophil-Lymphocyte ratio; Peripheral blood.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic changes in routine blood parameters of a severe COVID-19 case.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Sep;508:98-102. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.04.034. Epub 2020 May 13. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32405079 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of peripheral hematologic markers for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A multicenter, cross-sectional study.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Oct;34(10):e23475. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23475. Epub 2020 Jul 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32681559 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19 patients.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jul;84:106504. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106504. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32304994 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China.Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 28;71(15):762-768. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa248. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32161940 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal and infant outcomes of full-term pregnancy combined with COVID-2019 in Wuhan, China: retrospective case series.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020 Sep;302(3):545-551. doi: 10.1007/s00404-020-05573-8. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020. PMID: 32696241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Inflammatory Markers in Patients with COVID-19 Combined with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024 Oct 26;17:2535-2545. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S490281. eCollection 2024. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024. PMID: 39479559 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Characteristics of Lymphocyte Subsets and Their Predictive Value for Disease Progression and Prognosis in Primary Infection and Unvaccinated COVID-19 Patients.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Oct 10;17:4559-4577. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S478912. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39403609 Free PMC article.
-
Back to Basics: The Diagnostic Value of a Complete Blood Count in the Clinical Management of COVID-19.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Sep 2;14(17):1933. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14171933. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272717 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of NLR and PLR in COVID-19: A Multi-Cohort Validation Study.Infect Dis Ther. 2024 May;13(5):1147-1157. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-00967-6. Epub 2024 Apr 21. Infect Dis Ther. 2024. PMID: 38643431 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, a novel biomarker to predict the severity of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Intensive Care Soc. 2022 Feb;23(1):20-26. doi: 10.1177/1751143720969587. Epub 2020 Nov 2. J Intensive Care Soc. 2022. PMID: 38603090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Demirdal T., Sen P. The significance of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte-monocyte ratio in predicting peripheral arterial disease, peripheral neuropathy, osteomyelitis and amputation in diabetic foot infection. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018;144:118–125. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.08.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Diagnosis and treatment protocols of the novel coronavirus pneumonia (trial version 7). Beijing: National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China; Mar 3, 2020.Chinese.Available from: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb19....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

