COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review
- PMID: 32325252
- PMCID: PMC7169933
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108427
COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review
Abstract
In December 2019, a novel coronavirus, now named as SARS-CoV-2, caused a series of acute atypical respiratory diseases in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. The disease caused by this virus was termed COVID-19. The virus is transmittable between humans and has caused pandemic worldwide. The number of death tolls continues to rise and a large number of countries have been forced to do social distancing and lockdown. Lack of targeted therapy continues to be a problem. Epidemiological studies showed that elder patients were more susceptible to severe diseases, while children tend to have milder symptoms. Here we reviewed the current knowledge about this disease and considered the potential explanation of the different symptomatology between children and adults.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures
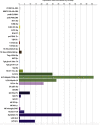
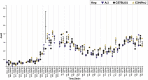
Comment in
-
Can Ticagrelor be used to prevent sepsis-induced coagulopathy in COVID-19?Clin Immunol. 2020 Jul;216:108468. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108468. Epub 2020 May 21. Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32445671 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Overview of lethal human coronaviruses.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jun 10;5(1):89. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0190-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32533062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scientific research progress of COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 in the first five months.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jun;24(12):6558-6570. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15364. Epub 2020 May 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32320516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune response in COVID-19: addressing a pharmacological challenge by targeting pathways triggered by SARS-CoV-2.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 May 29;5(1):84. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0191-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32467561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic dysregulation of ACE2 and interferon-regulated genes might suggest increased COVID-19 susceptibility and severity in lupus patients.Clin Immunol. 2020 Jun;215:108410. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108410. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32276140 Free PMC article.
-
Current pharmacological modalities for management of novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and the rationale for their utilization: A review.Rev Med Virol. 2020 Sep;30(5):e2136. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2136. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Rev Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32644275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunobiology and nanotherapeutics of severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2): a current update.Infect Dis (Lond). 2021 Aug;53(8):559-580. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2021.1916071. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Infect Dis (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33905282 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutic Candidates for COVID-19: A Poorly Understood Arena.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 17;11:585888. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.585888. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33041830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanding current guidelines for management of COVID-19 focusing on low- and middle-income countries.J Public Health Afr. 2022 Oct 11;13(3):1465. doi: 10.4081/jphia.2022.1465. eCollection 2022 Sep 7. J Public Health Afr. 2022. PMID: 36313927 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of tofacitinib therapy is critical to improving outcomes in severe-critical COVID-19 infection: A retrospective study from a tertiary care hospital.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Oct 28;101(43):e30975. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030975. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36316872 Free PMC article.
-
Highly regioselective 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of 3'-O-propargyl guanosine with nitrile oxide: An efficient method for the synthesis of guanosine containing isoxazole moiety.Tetrahedron Lett. 2020 Oct 29;61(44):152464. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2020.152464. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020. PMID: 32981977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ksiazek T.G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C.S., Zaki S.R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J.A., Lim W., Rollin P.E., Dowell S.F., Ling A.E., Humphrey C.D., Shieh W.J., Guarner J., Paddock C.D., Rota P., Fields B., DeRisi J., Yang J.Y., Cox N., Hughes J.M., LeDuc J.W., Bellini W.J., Anderson L.J., SW Group A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
-
- Li Q., Guan X., Wu P., Wang X., Zhou L., Tong Y., Ren R., Leung K.S.M., Lau E.H.Y., Wong J.Y., Xing X., Xiang N., Wu Y., Li C., Chen Q., Li D., Liu T., Zhao J., Liu M., Tu W., Chen C., Jin L., Yang R., Wang Q., Zhou S., Wang R., Liu H., Luo Y., Liu Y., Shao G., Li H., Tao Z., Yang Y., Deng Z., Liu B., Ma Z., Zhang Y., Shi G., Lam T.T.Y., Wu J.T., Gao G.F., Cowling B.J., Yang B., Leung G.M., Feng Z. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1199–1207. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang J., Litvinova M., Wang W., Wang Y., Deng X., Chen X., Li M., Zheng W., Yi L., Chen X., Wu Q., Liang Y., Wang X., Yang J., Sun K., Longini I.M., Jr., Halloran M.E., Wu P., Cowling B.J., Merler S., Viboud C., Vespignani A., Ajelli M., Yu H. Evolving epidemiology and transmission dynamics of coronavirus disease 2019 outside Hubei province, China: a descriptive and modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30230-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- JHUoMCr center Journal. 2020 https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

