Distribution of duodenal tuft cells is altered in pediatric patients with acute and chronic enteropathy
- PMID: 32307399
- PMCID: PMC10037909
- DOI: 10.2220/biomedres.41.113
Distribution of duodenal tuft cells is altered in pediatric patients with acute and chronic enteropathy
Abstract
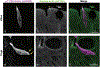
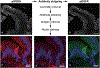
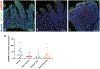
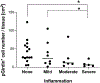
Clinical interest into the function of tuft cells in human intestine has increased in recent years. However, no quantitative study has examined intestinal tuft cells in pathological specimens from patients. This study quantified tuft cell density by using a recently identified marker, specific for tyrosine phosphorylation (pY1798) of girdin (also known as CCDC88A or GIV) in the duodenum of pediatric patients. Deidentified sections with pathological diagnosis of acute duodenitis, ulcer, or celiac disease, and age-matched normal control were analyzed under double-blind conditions. Immunostaining for pY1798-girdin demonstrated the distinct shape of tuft cells with and filopodia-like basolateral membrane structure and a small apical area, which densely expressed gamma-actin. As compared to normal tissues, the specimens diagnosed as celiac disease and duodenal ulcer had significantly fewer tuft cell numbers. In contrast, acute duodenitis showed varied population of tuft cells. The mucosa with severe inflammation showed lower tuft cell numbers than the specimens with none to mild inflammation. These results suggest that loss of tuft cells may be involved in prolonged inflammation in the duodenal mucosa and disrupted mucosal integrity. pY1798-girdin and gamma-actin are useful markers for investigating the distribution and morphologies of human intestinal tuft cells under healthy and pathological conditions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tyrosine Phosphorylation of an Actin-Binding Protein Girdin Specifically Marks Tuft Cells in Human and Mouse Gut.J Histochem Cytochem. 2017 Jun;65(6):347-366. doi: 10.1369/0022155417702586. Epub 2017 Apr 4. J Histochem Cytochem. 2017. PMID: 28375676 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Anti-phospho-girdin Antibodies to Visualize Intestinal Tuft Cells in Free-Floating Mouse Jejunum Cryosections.J Vis Exp. 2018 Mar 21;(133):57475. doi: 10.3791/57475. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 29630055 Free PMC article.
-
Lysozyme-rich mucus metaplasia in duodenal crypts supersedes Paneth cells in celiac disease.Virchows Arch. 2011 Sep;459(3):339-46. doi: 10.1007/s00428-011-1129-3. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Virchows Arch. 2011. PMID: 21769618
-
The duodenal mucosa in health and disease. A clinical and experimental study.Surg Annu. 1989;21:157-80. Surg Annu. 1989. PMID: 2655122 Review.
-
Duodenitis.Clin Gastroenterol. 1978 Sep;7(3):635-50. Clin Gastroenterol. 1978. PMID: 361306 Review.
Cited by
-
Luminal Chemosensory Cells in the Small Intestine.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 22;13(11):3712. doi: 10.3390/nu13113712. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34835968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic tuft cell expansion during gastric metaplasia and dysplasia.J Pathol Clin Res. 2024 Jan;10(1):e352. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.352. Epub 2023 Dec 20. J Pathol Clin Res. 2024. PMID: 38117182 Free PMC article.
-
Tuft Cells and Their Role in Intestinal Diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 14;13:822867. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.822867. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35237268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Differentiated Intestinal Epithelial Cells Using Immunostaining and Fluorescence Microscopy.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2650:17-34. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3076-1_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37310620
-
Tuft Cells: Context- and Tissue-Specific Programming for a Conserved Cell Lineage.Annu Rev Pathol. 2023 Jan 24;18:311-335. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-042320-112212. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36351364 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bezencon C, le Coutre J and Damak S (2007) Taste-signaling proteins are coexpressed in solitary intestinal epithelial cells. Clieni Senses 32, 41–19. - PubMed
-
- Fleming JO and Weinstock JV (2015) Clinical trials of helminth therapy in autoimmune diseases: rationale and findings. Parasite Immunol 37, 277–292. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

