COVID-19 and emerging viral infections: The case for interferon lambda
- PMID: 32289152
- PMCID: PMC7155807
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20200653
COVID-19 and emerging viral infections: The case for interferon lambda
Abstract
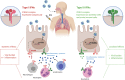
With the first reports on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the scientific community working in the field of type III IFNs (IFN-λ) realized that this class of IFNs could play an important role in this and other emerging viral infections. In this Viewpoint, we present our opinion on the benefits and potential limitations of using IFN-λ to prevent, limit, and treat these dangerous viral infections.
© 2020 Prokunina-Olsson et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiviral Activity of Type I, II, and III Interferons Counterbalances ACE2 Inducibility and Restricts SARS-CoV-2.mBio. 2020 Sep 10;11(5):e01928-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01928-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32913009 Free PMC article.
-
Type III interferons disrupt the lung epithelial barrier upon viral recognition.Science. 2020 Aug 7;369(6504):706-712. doi: 10.1126/science.abc3545. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Science. 2020. PMID: 32527925 Free PMC article.
-
Type I and Type III Interferons Restrict SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Human Airway Epithelial Cultures.J Virol. 2020 Sep 15;94(19):e00985-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00985-20. Print 2020 Sep 15. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32699094 Free PMC article.
-
Type I and Type III Interferons - Induction, Signaling, Evasion, and Application to Combat COVID-19.Cell Host Microbe. 2020 Jun 10;27(6):870-878. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.008. Epub 2020 May 27. Cell Host Microbe. 2020. PMID: 32464097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 entry in host cells-multiple targets for treatment and prevention.Biochimie. 2020 Aug;175:93-98. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 May 29. Biochimie. 2020. PMID: 32479856 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The interaction of innate immune and adaptive immune system.MedComm (2020). 2024 Sep 15;5(10):e714. doi: 10.1002/mco2.714. eCollection 2024 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39286776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Narrative Overview of Coronavirus Infection: Clinical Signs and Symptoms, Viral Entry and Replication, Treatment Modalities, and Management.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(21):1883-1916. doi: 10.2174/0115680266296095240529114058. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38859776 Review.
-
Omicron Spike confers enhanced infectivity and interferon resistance to SARS-CoV-2 in human nasal tissue.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 30;15(1):889. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45075-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38291024 Free PMC article.
-
Participation of Single-Nucleotide Variants in IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 in the Immune Response against SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review.Pathogens. 2023 Nov 6;12(11):1320. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111320. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type III interferon exerts thymic stromal lymphopoietin in mediating adaptive antiviral immune response.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 22;14:1250541. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1250541. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37809098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AI39512/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- FC001206/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- FC001206/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R21 AG064479/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 206200/Z/17/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AI139512/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI121066/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG064479-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U117597139/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK115217/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI201700100/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- FC001206/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

