Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19
- PMID: 32233013
- PMCID: PMC7228407
- DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.3319
Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19
Abstract
Backgound: To figure out whether diabetes is a risk factor influencing the progression and prognosis of 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Methods: A total of 174 consecutive patients confirmed with COVID-19 were studied. Demographic data, medical history, symptoms and signs, laboratory findings, chest computed tomography (CT) as well the treatment measures were collected and analysed.
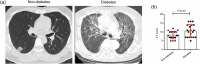
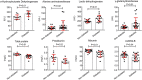
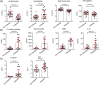
Results: We found that COVID-19 patients without other comorbidities but with diabetes (n = 24) were at higher risk of severe pneumonia, release of tissue injury-related enzymes, excessive uncontrolled inflammation responses and hypercoagulable state associated with dysregulation of glucose metabolism. Furthermore, serum levels of inflammation-related biomarkers such as IL-6, C-reactive protein, serum ferritin and coagulation index, D-dimer, were significantly higher (P < .01) in diabetic patients compared with those without, suggesting that patients with diabetes are more susceptible to an inflammatory storm eventually leading to rapid deterioration of COVID-19.
Conclusions: Our data support the notion that diabetes should be considered as a risk factor for a rapid progression and bad prognosis of COVID-19. More intensive attention should be paid to patients with diabetes, in case of rapid deterioration.
Keywords: COVID-19; diabetes; prognosis.
© 2020 The Authors. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest regarding this publication.
Figures
Comment in
-
Technology Gap Deepened by Coronavirus Pandemic.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020 Jul;14(4):774-775. doi: 10.1177/1932296820929390. Epub 2020 May 27. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32460626 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Serum amyloid A protein has been undervalued as a biomarker of COVID-19.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021 Jan;37(1):e3376. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3376. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32588938 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diabetes and Covid-19: An interplay difficult to dissect.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021 Jan;37(1):e3387. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3387. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32818297 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Impact of glycemic control in diabetes mellitus on management of COVID-19 infection.Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2020 Sep;40(3):340-345. doi: 10.1007/s13410-020-00868-7. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2020. PMID: 32905072 Free PMC article.
-
Basic Predictive Risk Factors for Cytokine Storms in COVID-19 Patients.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 10;12:745515. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.745515. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34858403 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics, laboratory abnormalities and CT findings of COVID-19 patients and risk factors of severe disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Feb;10(2):1928-1949. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1863. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33548996
-
Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020 Jun 25;58(7):1021-1028. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0369. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32286245 Review.
-
Covid-19: The Rollercoaster of Fibrin(Ogen), D-Dimer, Von Willebrand Factor, P-Selectin and Their Interactions with Endothelial Cells, Platelets and Erythrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 21;21(14):5168. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145168. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32708334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the receptor for advanced glycation end products in the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection in diabetic patients.Diabetol Int. 2024 Jul 26;15(4):732-744. doi: 10.1007/s13340-024-00746-1. eCollection 2024 Oct. Diabetol Int. 2024. PMID: 39469543 Review.
-
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Aggravates Complement Dysregulation and Affects Cortisol Response in Patients with Post-COVID-19.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Oct 19;17:3849-3861. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S480457. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39449862 Free PMC article.
-
Glycemic Management in Patients with COVID-19 Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: Evaluation of Glycemic Control and Drug Therapy.Can J Hosp Pharm. 2024 Oct 9;77(4):e3553. doi: 10.4212/cjhp.3553. eCollection 2024. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39386973
-
Looking for the ideal medication for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a narrative review.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Sep 6;11:1439696. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1439696. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39314771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STUDY HYPOTHESIS: AGE, GENDER, PRESENCE OF DIABETES MELLITUS OR HYPERTENSION, AND ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE DRUGS ARE INDEPENDENT RISK FACTORS FOR COVID-19 MORTALITY.Acta Clin Croat. 2023 Nov;62(3):447-456. doi: 10.20471/acc.2023.62.03.6. Acta Clin Croat. 2023. PMID: 39310686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, Karran E, Christie G, Turner AJ. A human homolog of angiotensin‐converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril‐insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(43):33238‐33243. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

