Role of Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 32211348
- PMCID: PMC7074856
- DOI: 10.2147/ITT.S243636
Role of Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
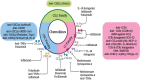
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most prevalent autoimmune diseases and a prototypic inflammatory disease, affecting the small joints of the hands and feet. Chemokines and chemokine receptors play a critical role in RA pathogenesis via immune cells recruitment. Several chemokines and chemokine receptors are abundant in the peripheral blood and in the local inflamed joints of RA. Furthermore, synthetic and biologics disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs have been reported to affect chemokines expression. Thus, many studies have focused on targeting chemokines and chemokine receptors, where some have shown positive promising results. However, most of the chemokine blockers in human trials of RA treatment displayed some failures that can be attributed to several reasons in their structures and binding affinities. Nevertheless, targeting chemokines will continue to be under development, in order to improve their therapeutic potentials in RA and other autoimmune diseases. In this review we provide an up-to-date knowledge regarding the role of chemokines and chemokine receptors in RA with an emphasis on their activities on immune cells. We also discussed the effects of drugs targeting those molecules in RA. This knowledge might provide impetus for developing new therapeutic modalities to treat this chronic disease.
Keywords: chemokine receptors; chemokines; drugs; immunotargets; immunotherapy; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2020 Elemam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chemokines and chemokine receptors as promising targets in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 13;14:1100869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1100869. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36860872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successes and failures of chemokine-pathway targeting in rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016 Jan;12(1):5-13. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.157. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26607389 Review.
-
Chemokine and chemokine receptor blockade in arthritis, a prototype of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.Neth J Med. 2011 Sep;69(9):356-66. Neth J Med. 2011. PMID: 21978977 Review.
-
Chemokines and chemokine receptors as novel therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): inhibitory effects of traditional Chinese medicinal components.Cell Mol Immunol. 2004 Oct;1(5):336-42. Cell Mol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 16285892 Review.
-
Targeting the Chemokine System in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Vasculitis.JMA J. 2020 Jul 15;3(3):182-192. doi: 10.31662/jmaj.2020-0019. Epub 2020 Jul 13. JMA J. 2020. PMID: 33150252 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Cytokine Inhibition Modulates Activation and Homing Receptors of Peripheral Memory B Cell Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 11;11:572475. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.572475. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33042152 Free PMC article.
-
Na-AIP-1 secreted by human hookworms suppresses collagen-induced arthritis.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Apr;30(2):527-535. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00909-5. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35031905
-
The Impacts of IL1R1 and IL1R2 Genetic Variants on Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in the Chinese Han Population: A Case-Control Study.Int J Gen Med. 2021 May 28;14:2147-2159. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S291395. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34093035 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SYK and cSrc kinases can protect bone and cartilage in preclinical models of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 30;11(1):23120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02568-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34848799 Free PMC article.
-
Development of tolerance to chemokine receptor antagonists: current paradigms and the need for further investigation.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 28;14:1184014. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1184014. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37575219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

