Long-term storage of lipid-like nanoparticles for mRNA delivery
- PMID: 32206737
- PMCID: PMC7078456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.03.001
Long-term storage of lipid-like nanoparticles for mRNA delivery
Abstract
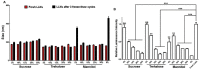
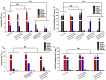
Lipid-like nanoparticles (LLNs) have been extensively explored for messenger RNA (mRNA) delivery in various biomedical applications. However, the long-term storage of these nanoparticles is still a challenge for their clinical translation. In this study, we investigated a series of conditions for the long-term storage of LLNs with encapsulation of mRNA. We evaluated the stability of LLNs with different concentrations of cryoprotectants (sucrose, trehalose or mannitol) under the conditions of freezing or lyophilization processes. Through in vitro and in vivo mRNA delivery studies, we identified the optimal storage condition, and found that the addition with 5% (w/v) sucrose or trehalose to LLNs could remain their mRNA delivery efficiency for at least three months in the liquid nitrogen storage condition.
Keywords: Lipid-like nanoparticles; Long-term storage; mRNA delivery.
© 2020 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures
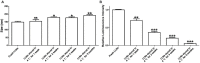
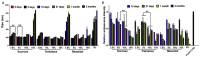
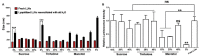
Similar articles
-
Achieving long-term stability of lipid nanoparticles: examining the effect of pH, temperature, and lyophilization.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Dec 30;12:305-315. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S123062. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 28115848 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Cryoprotectants and Storage Conditions on the Transfection Efficiency, Stability, and Safety of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for mRNA and DNA Delivery.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Jul;12(18):e2203022. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202203022. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 36906918 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of local structural transformation of lipid-like compounds on delivery of messenger RNA.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 26;6:22137. doi: 10.1038/srep22137. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26916931 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation materials for RNA-lipid nanoparticles: lyophilization and targeted transfection.J Mater Chem B. 2023 Jun 14;11(23):5083-5093. doi: 10.1039/d3tb00308f. J Mater Chem B. 2023. PMID: 37221913 Review.
-
Optimal delivery strategies for nanoparticle-mediated mRNA delivery.J Mater Chem B. 2023 Mar 8;11(10):2063-2077. doi: 10.1039/d2tb02455a. J Mater Chem B. 2023. PMID: 36794598 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient hepatic delivery and protein expression enabled by optimized mRNA and ionizable lipid nanoparticle.Bioact Mater. 2020 Jul 13;5(4):1053-1061. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.07.003. eCollection 2020 Dec. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 32691013 Free PMC article.
-
Applications and challenges of biomaterial mediated mRNA delivery.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022;3(4):428-444. doi: 10.37349/etat.2022.00093. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022. PMID: 36071982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lessons learned from COVID-19 pandemic: Vaccine platform is a key player.Process Biochem. 2023 Jan;124:269-279. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2022.12.002. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Process Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36514356 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterial-Mediated Protein Expression Induced by Peptide-mRNA Nanoparticles Embedded in Lyophilized Collagen Scaffolds.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 2;14(8):1619. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081619. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015245 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of mRNA Lipid Nanoparticles by Electron Density Mapping Reconstruction: X-ray Scattering with Density from Solution Scattering (DENSS) Algorithm.Pharm Res. 2024 Mar;41(3):501-512. doi: 10.1007/s11095-024-03671-9. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38326530
References
-
- Hajj K.A., Whitehead K.A. Tools for translation: non-viral materials for therapeutic mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017;2:1–17.
-
- Granot-Matok Y., Kon E., Dammes N., Mechtinger G., Peer D. Therapeutic mRNA delivery to leukocytes. J. Contr. Release. 2019;305:165–175. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

