Sodium-glucose cotransporters: Functional properties and pharmaceutical potential
- PMID: 32196987
- PMCID: PMC7378437
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13255
Sodium-glucose cotransporters: Functional properties and pharmaceutical potential
Abstract
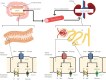
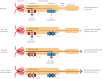
Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide, and an essential source of energy for most living cells. Glucose transport across the cell membrane is mediated by two types of transporters: facilitative glucose transporters (gene name: solute carrier 2A) and sodium-glucose cotransporters (SGLTs; gene name: solute carrier 5A). Each transporter has its own substrate specificity, distribution, and regulatory mechanisms. Recently, SGLT1 and SGLT2 have attracted much attention as therapeutic targets for various diseases. This review addresses the basal and functional properties of glucose transporters and SGLTs, and describes the pharmaceutical potential of SGLT1 and SGLT2.
Keywords: Antidiabetic drugs; Sodium-glucose cotransporter 1; Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Ryuhei Sano and Yuichi Shinozaki are employees of Japan Tobacco Inc. Takeshi Ohta declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporters Family: Current Evidence, Clinical Applications and Perspectives.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 May 25;28(5):103. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2805103. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37258483 Review.
-
SGLT1 inhibition: Pros and cons.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 5;838:153-156. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.09.019. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30240793 Review.
-
SGLT1 in pancreatic α cells regulates glucagon secretion in mice, possibly explaining the distinct effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on plasma glucagon levels.Mol Metab. 2019 Jan;19:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 27. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30416006 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Products as Lead Compounds for Sodium Glucose Cotransporter (SGLT) Inhibitors.Planta Med. 2017 Aug;83(12-13):985-993. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-106050. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Planta Med. 2017. PMID: 28395363 Review.
-
Sodium-coupled glucose transport, the SLC5 family, and therapeutically relevant inhibitors: from molecular discovery to clinical application.Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1177-1206. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02433-x. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Pflugers Arch. 2020. PMID: 32767111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Risks and Benefits of SGLT-2 Inhibitors for Type 1 Diabetes Patients Using Automated Insulin Delivery Systems-A Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 6;25(4):1972. doi: 10.3390/ijms25041972. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early use of SGLT2 inhibitors reduces the progression of diabetic kidney disease: a retrospective cohort study.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Sep 15;16(9):4967-4978. doi: 10.62347/ARYA8831. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39398587 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Glucose and Fatty Acid Metabolism in the Context of Anthracycline and Taxane-Based (Neo)Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Carcinomas.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 31;12:850401. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.850401. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35433453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling of SGLT1 in Reconstituted Systems Reveals Apparent Ion-Dependencies of Glucose Uptake and Strengthens the Notion of Water-Permeable Apo States.Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 15;13:874472. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.874472. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35784872 Free PMC article.
-
TXNIP interaction with GLUT1 depends on PI(4,5)P2.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021 Dec 1;1863(12):183757. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183757. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021. PMID: 34478732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mueckler M. Facilitative glucose transporters. Eur J Biochem 1994; 219: 713–725. - PubMed
-
- Joost HG, Thorens B. The extended GLUT‐family of sugar/polyol transport facilitators: nomenclature, sequence characteristics, and potential function of its novel members (review). Mol Membr Biol 2001; 18: 247–256. - PubMed
-
- Wright EM. Renal Na(+)‐glucose cotransporters. Am J Physiol Renal Physio 2001; 280: F10–F18. - PubMed
-
- Wood IS, Trayhurn P. Glucose transporters (GLUT and SGLT): expanded families of sugar transport proteins. Br J Nutr 2003; 89: 3–9. - PubMed
-
- Scheepers A, Joost HG, Schurmann A. The glucose transporter families SGLT and GLUT: molecular basis of normal and aberrant function. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2004; 28: 364–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

