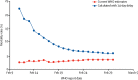
Real estimates of mortality following COVID-19 infection
- PMID: 32171390
- PMCID: PMC7118515
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30195-X
Real estimates of mortality following COVID-19 infection
Figures
Comment in
-
Estimating case fatality rates of COVID-19.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Jul;20(7):775. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30245-0. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32243813 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Estimating case fatality rates of COVID-19.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Jul;20(7):774-775. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30246-2. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32243815 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Authors' reply.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Jul;20(7):775-776. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30255-3. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32243816 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Can reasoned mass testing impact covid-19 outcomes in wide community contexts? An evidence-based opinion.Pathog Glob Health. 2021 May;115(3):203-207. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2021.1878444. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Pathog Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 33686907 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
The gendered dimensions of COVID-19.Lancet. 2020 Apr 11;395(10231):1168. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30823-0. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32278370 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Solidarity with China as it holds the global front line during COVID-19 outbreak.J Travel Med. 2020 May 18;27(3):taaa027. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taaa027. J Travel Med. 2020. PMID: 32125432 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Relation between BCG coverage rate and COVID-19 infection worldwide.Med Hypotheses. 2020 Sep;142:109816. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109816. Epub 2020 May 6. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 32408071 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
SARS-CoV-2 transmission: a sociological review.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Oct 7;148:e242. doi: 10.1017/S095026882000240X. Epidemiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 33023703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strengthening accountability of the global health metrics enterprise.Lancet. 2020 May 2;395(10234):1452-1456. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30416-5. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32305072 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Asymptomatic COVID-19: disease tolerance with efficient anti-viral immunity against SARS-CoV-2.EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Jun 7;13(6):e14045. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114045. Epub 2021 May 27. EMBO Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33961735 Free PMC article.
-
An updated review of the association of host genetic factors with susceptibility and resistance to COVID-19.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Jan;236(1):49-54. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29868. Epub 2020 Jun 15. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32542735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Cross Talk Between SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding and Replication Machinery in the Human Host.Front Physiol. 2020 Jun 30;11:802. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00802. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32695025 Free PMC article.
-
End of Life Intervention Program During COVID-19 in Vall d'Hebron University Hospital.Front Psychiatry. 2021 May 3;12:608973. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.608973. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34040548 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that contributed to burnout among intensive care nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: A constructivist grounded theory.Aust Crit Care. 2023 Jan;36(1):19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.aucc.2022.11.002. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Aust Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 36437164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Situation Report—41. March 1, 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2...
-
- WHO Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Feb, 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-china-joint-mis...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical