Recent advances in dopaminergic strategies for the treatment of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 32112042
- PMCID: PMC7471472
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-020-0365-y
Recent advances in dopaminergic strategies for the treatment of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
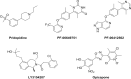
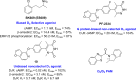
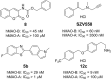
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common progressive neurodegenerative disease worldwide. However, there is no available therapy reversing the neurodegenerative process of PD. Based on the loss of dopamine or dopaminergic dysfunction in PD patients, most of the current therapies focus on symptomatic relief to improve patient quality of life. As dopamine replacement treatment remains the most effective symptomatic pharmacotherapy for PD, herein we provide an overview of the current pharmacotherapies, summarize the clinical development status of novel dopaminergic agents, and highlight the challenge and opportunity of emerging preclinical dopaminergic approaches aimed at managing the features and progression of PD.
Keywords: D1 receptor; D2 receptor; Parkinson’s disease; allosteric modulator; dopamine; drug discovery and development; multitarget; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The current status of pharmacotherapy for the treatment of Parkinson's disease: transition from single-target to multitarget therapy.Drug Discov Today. 2019 Sep;24(9):1769-1783. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 May 16. Drug Discov Today. 2019. PMID: 31102728 Review.
-
Parkinson's disease pharmacogenomics: new findings and perspectives.Pharmacogenomics. 2014 Jun;15(9):1253-71. doi: 10.2217/pgs.14.93. Pharmacogenomics. 2014. PMID: 25141900
-
Dopaminergic properties and experimental anti-parkinsonian effects of IPX750 in rodent models of Parkinson disease.Clin Neuropharmacol. 2004 Mar-Apr;27(2):63-73. doi: 10.1097/00002826-200403000-00004. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15252266
-
Treatment of Parkinson's disease: what's in the non-dopaminergic pipeline?Neurotherapeutics. 2014 Jan;11(1):34-46. doi: 10.1007/s13311-013-0239-9. Neurotherapeutics. 2014. PMID: 24310604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of indolylpiperazinylpyrimidines with dual-target profiles at adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptors for Parkinson's disease treatment.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 5;13(1):e0188212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188212. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29304113 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Arbutin effectively ameliorates the symptoms of Parkinson's disease: the role of adenosine receptors and cyclic adenosine monophosphate.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Oct;16(10):2030-2040. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.308102. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33642391 Free PMC article.
-
Empagliflozin attenuates neurodegeneration through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and modulation of α-synuclein and Parkin levels in rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease in rats.Saudi Pharm J. 2022 Jun;30(6):863-873. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.03.005. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Saudi Pharm J. 2022. PMID: 35812142 Free PMC article.
-
Insomnia in Parkinson's Disease: Causes, Consequences, and Therapeutic Approaches.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Aug 5. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04400-4. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39103716 Review.
-
Current Advances of Plant-Based Vaccines for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 20;15(2):711. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020711. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36840033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin protects against rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease in mice by inhibiting microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation and alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction.Heliyon. 2023 May 11;9(5):e16195. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16195. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37234646 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials