TRPV1 activation alleviates cognitive and synaptic plasticity impairments through inhibiting AMPAR endocytosis in APP23/PS45 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 32061032
- PMCID: PMC7059138
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13113
TRPV1 activation alleviates cognitive and synaptic plasticity impairments through inhibiting AMPAR endocytosis in APP23/PS45 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
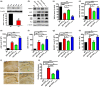
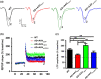
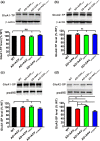
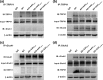
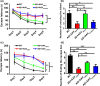
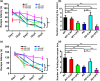
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common causes of neurodegenerative diseases in the elderly. The accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides is one of the pathological hallmarks of AD and leads to the impairments of synaptic plasticity and cognitive function. The transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), a nonselective cation channel, is involved in synaptic plasticity and memory. However, the role of TRPV1 in AD pathogenesis remains largely elusive. Here, we reported that the expression of TRPV1 was decreased in the brain of APP23/PS45 double transgenic AD model mice. Genetic upregulation of TRPV1 by adeno-associated virus (AAV) inhibited the APP processing and Aβ deposition in AD model mice. Meanwhile, upregulation of TRPV1 ameliorated the deficits of hippocampal CA1 long-term potentiation (LTP) and spatial learning and memory through inhibiting GluA2-containing α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR) endocytosis. Furthermore, pharmacological activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin (1 mg/kg, i.p.), an agonist of TRPV1, dramatically reversed the impairments of hippocampal CA1 LTP and spatial learning and memory in AD model mice. Taken together, these results indicate that TRPV1 activation effectively ameliorates cognitive and synaptic functions through inhibiting AMPAR endocytosis in AD model mice and could be a novel molecule for AD treatment.
Keywords: AMPA receptor endocytosis; Alzheimer's disease; TRPV1; capsaicin; learning and memory; long-term potentiation.
© 2020 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Capsaicin Attenuates Amyloid-β-Induced Synapse Loss and Cognitive Impairments in Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;59(2):683-694. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170337. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28671132
-
Ca2+-permeable TRPV1 pain receptor knockout rescues memory deficits and reduces amyloid-β and tau in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Jan 15;29(2):228-237. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz276. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 31814000
-
miR-181a negatively modulates synaptic plasticity in hippocampal cultures and its inhibition rescues memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Aging Cell. 2020 Mar;19(3):e13118. doi: 10.1111/acel.13118. Epub 2020 Feb 22. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 32087004 Free PMC article.
-
Novel crosstalk mechanisms between GluA3 and Epac2 in synaptic plasticity and memory in Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Feb;191:106389. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106389. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 38142840 Review.
-
Synaptic Alterations in Mouse Models for Alzheimer Disease-A Special Focus on N-Truncated Abeta 4-42.Molecules. 2018 Mar 21;23(4):718. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040718. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29561816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Model of Neuroinflammation: Mechanisms of Action, Research Application and Future Directions for Its Use.Molecules. 2022 Aug 26;27(17):5481. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175481. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of TRPV1 on Pathogenesis and Therapy of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Molecules. 2023 Dec 28;29(1):181. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010181. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetylation of AMPA Receptors Regulates Receptor Trafficking and Rescues Memory Deficits in Alzheimer's Disease.iScience. 2020 Aug 15;23(9):101465. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101465. eCollection 2020 Sep 25. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32861999 Free PMC article.
-
Diet and lifestyle impact the development and progression of Alzheimer's dementia.Front Nutr. 2023 Jun 29;10:1213223. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1213223. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37457976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin in Various Neurodegenerative Diseases with Special Focus on Nrf2 Signaling.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(13):1693-1707. doi: 10.2174/0113892010277933231122111244. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38173062 Review.
References
-
- Beyreuther, K. , & Masters, C. L. (1991). Amyloid precursor protein (APP) and beta A4 amyloid in the etiology of Alzheimer's disease: Precursor‐product relationships in the derangement of neuronal function. Brain Pathology, 1(4), 241–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

