TGF-β inhibition combined with cytotoxic nanomedicine normalizes triple negative breast cancer microenvironment towards anti-tumor immunity
- PMID: 32042344
- PMCID: PMC6993226
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.36936
TGF-β inhibition combined with cytotoxic nanomedicine normalizes triple negative breast cancer microenvironment towards anti-tumor immunity
Abstract
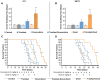
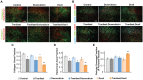
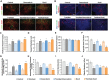
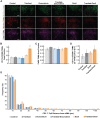
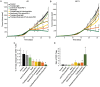
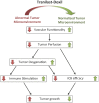
Tumor normalization strategies aim to improve tumor blood vessel functionality (i.e., perfusion) by reducing the hyper-permeability of tumor vessels or restoring compressed vessels. Despite progress in strategies to normalize the tumor microenvironment (TME), their combinatorial antitumor effects with nanomedicine and immunotherapy remain unexplored. Methods: Here, we re-purposed the TGF-β inhibitor tranilast, an approved anti-fibrotic and antihistamine drug, and combined it with Doxil nanomedicine to normalize the TME, increase perfusion and oxygenation, and enhance anti-tumor immunity. Specifically, we employed two triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) mouse models to primarily evaluate the therapeutic and normalization effects of tranilast combined with doxorubicin and Doxil. We demonstrated the optimized normalization effects of tranilast combined with Doxil and extended our analysis to investigate the effect of TME normalization to the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Results: Combination of tranilast with Doxil caused a pronounced reduction in extracellular matrix components and an increase in the intratumoral vessel diameter and pericyte coverage, indicators of TME normalization. These modifications resulted in a significant increase in tumor perfusion and oxygenation and enhanced treatment efficacy as indicated by the notable reduction in tumor size. Tranilast further normalized the immune TME by restoring the infiltration of T cells and increasing the fraction of T cells that migrate away from immunosuppressive cancer-associated fibroblasts. Furthermore, we found that combining tranilast with Doxil nanomedicine, significantly improved immunostimulatory M1 macrophage content in the tumorigenic tissue and improved the efficacy of the immune checkpoint blocking antibodies anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4. Conclusion: Combinatorial treatment of tranilast with Doxil optimizes TME normalization, improves immunostimulation and enhances the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Keywords: immunostimulation; immunotherapy; nanomedicine; normalization; tumor microenvironment; vascular perfusion.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tranilast-induced stress alleviation in solid tumors improves the efficacy of chemo- and nanotherapeutics in a size-independent manner.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 10;7:46140. doi: 10.1038/srep46140. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28393881 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronous targeted delivery of TGF-β siRNA to stromal and tumor cells elicits robust antitumor immunity against triple-negative breast cancer by comprehensively remodeling the tumor microenvironment.Biomaterials. 2023 Oct;301:122253. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122253. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Biomaterials. 2023. PMID: 37536040
-
Sonic-hedgehog pathway inhibition normalizes desmoplastic tumor microenvironment to improve chemo- and nanotherapy.J Control Release. 2017 Sep 10;261:105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.06.022. Epub 2017 Jun 27. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28662901 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Immunotherapy in Urologic Cancer: Evolving Roles for Targeting of CTLA-4, PD-1/PD-L1, and HLA-G.Eur Urol. 2015 Aug;68(2):267-79. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.02.032. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25824720 Review.
-
Immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer: Existing challenges and exciting prospects.Drug Resist Updat. 2017 May;32:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Drug Resist Updat. 2017. PMID: 29145974 Review.
Cited by
-
m6A regulator-mediated methylation modification highlights immune infiltration patterns for predicting risk in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jul;149(7):3661-3680. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04255-z. Epub 2022 Aug 16. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 35972694
-
Nanoparticle-mediated TRPV1 channel blockade amplifies cancer thermo-immunotherapy via heat shock factor 1 modulation.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 29;14(1):2498. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38128-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37120615 Free PMC article.
-
Development a m6A regulators characterized by the immune cell infiltration in stomach adenocarcinoma for predicting the prognosis and immunotherapy response.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Mar 17;15(6):1944-1963. doi: 10.18632/aging.204574. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37019148 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy in soft tissue and bone sarcoma: unraveling the barriers to effectiveness.Theranostics. 2022 Aug 15;12(14):6106-6129. doi: 10.7150/thno.72800. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36168619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compressive stresses in cancer: characterization and implications for tumour progression and treatment.Nat Rev Cancer. 2024 Nov;24(11):768-791. doi: 10.1038/s41568-024-00745-z. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39390249 Review.
References
-
- Jain RK. Taming vessels to treat cancer. Scientific American. 2008;298:56–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

