Temporal dynamics of protein complex formation and dissociation during human cytomegalovirus infection
- PMID: 32041945
- PMCID: PMC7010728
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-14586-5
Temporal dynamics of protein complex formation and dissociation during human cytomegalovirus infection
Abstract
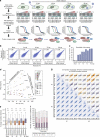
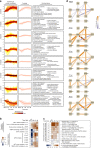
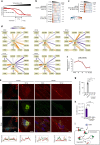
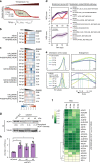
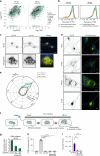
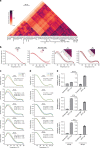
The co-evolution and co-existence of viral pathogens with their hosts for millions of years is reflected in dynamic virus-host protein-protein interactions (PPIs) that are intrinsic to the spread of infections. Here, we investigate the system-wide dynamics of protein complexes throughout infection with the herpesvirus, human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). Integrating thermal shift assays and mass spectrometry quantification with virology and microscopy, we monitor the temporal formation and dissociation of hundreds of functional protein complexes and the dynamics of host-host, virus-host, and virus-virus PPIs. We establish pro-viral roles for cellular protein complexes and translocating proteins. We show the HCMV receptor integrin beta 1 dissociates from extracellular matrix proteins, becoming internalized with CD63, which is necessary for virus production. Moreover, this approach facilitates characterization of essential viral proteins, such as pUL52. This study of temporal protein complex dynamics provides insights into mechanisms of HCMV infection and a resource for biological and therapeutic studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The life cycle and pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus infection: lessons from proteomics.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014 Dec;11(6):697-711. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2014.971116. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25327590 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus pUL37x1 Is Important for Remodeling of Host Lipid Metabolism.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00843-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00843-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31391267 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein-Initiated Signaling Mediates the Aberrant Activation of Akt.J Virol. 2020 Jul 30;94(16):e00167-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00167-20. Print 2020 Jul 30. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32493823 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Strategies to Maintain and Promote mRNA Translation.Viruses. 2016 Apr 13;8(4):97. doi: 10.3390/v8040097. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27089357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus riding the cell cycle.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Jun;204(3):409-19. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0396-z. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25776080 Review.
Cited by
-
Digital image processing technology under backpropagation neural network and K-Means Clustering algorithm on nitrogen utilization rate of Chinese cabbages.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 31;16(3):e0248923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248923. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2023 Aug 24;18(8):e0290865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290865 PMID: 33788875 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Progress Identifying and Analyzing the Human Proteome: 2021 Metrics from the HUPO Human Proteome Project.J Proteome Res. 2021 Dec 3;20(12):5227-5240. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.1c00590. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Proteome Res. 2021. PMID: 34670092 Free PMC article.
-
Target Discovery for Host-Directed Antiviral Therapies: Application of Proteomics Approaches.mSystems. 2021 Oct 26;6(5):e0038821. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00388-21. Epub 2021 Sep 14. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34519533 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024 May 14:10.1002/mas.21887. doi: 10.1002/mas.21887. Online ahead of print. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024. PMID: 38742660 Review.
-
A network view of human immune system and virus-human interaction.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 26;13:997851. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.997851. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389817 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

