Glucose-responsive insulin patch for the regulation of blood glucose in mice and minipigs
- PMID: 32015407
- PMCID: PMC7231631
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-019-0508-y
Glucose-responsive insulin patch for the regulation of blood glucose in mice and minipigs
Abstract
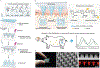
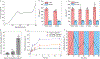
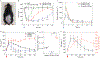
Glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems that mimic pancreatic endocrine function could enhance health and improve quality of life for people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes with reduced β-cell function. However, insulin delivery systems with rapid in vivo glucose-responsive behaviour typically have limited insulin-loading capacities and cannot be manufactured easily. Here, we show that a single removable transdermal patch, bearing microneedles loaded with insulin and a non-degradable glucose-responsive polymeric matrix, and fabricated via in situ photopolymerization, regulated blood glucose in insulin-deficient diabetic mice and minipigs (for minipigs >25 kg, glucose regulation lasted >20 h with patches of ~5 cm2). Under hyperglycaemic conditions, phenylboronic acid units within the polymeric matrix reversibly form glucose-boronate complexes that-owing to their increased negative charge-induce the swelling of the polymeric matrix and weaken the electrostatic interactions between the negatively charged insulin and polymers, promoting the rapid release of insulin. This proof-of-concept demonstration may aid the development of other translational stimuli-responsive microneedle patches for drug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
Z.G., J.Y. and G.C. have applied for patents related to this study. Z.G. is a scientific co-founder of Zenomics Inc. R.L. and J.B.B. are Scientific Advisory Board members of Zenomics Inc. J.Y., Y.Z., W.M. and Y.Y. are full-time employees of Zenomics Inc. R.L. discloses potential competing interests due to his affiliation with Zenomics Inc. For a list of entities with which R.L. is involved, compensated or uncompensated, see
Figures
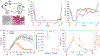
Similar articles
-
Glucose-responsive microneedle patch for closed-loop dual-hormone delivery in mice and pigs.Sci Adv. 2022 Dec 2;8(48):eadd3197. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.add3197. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36449622 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-Responsive Microneedle Patch with High Insulin Loading Capacity for Prolonged Glycemic Control in Mice and Minipigs.ACS Nano. 2024 Sep 11. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c05562. Online ahead of print. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39259604
-
Charge-switchable polymeric complex for glucose-responsive insulin delivery in mice and pigs.Sci Adv. 2019 Jul 10;5(7):eaaw4357. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw4357. eCollection 2019 Jul. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31309150 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-Responsive Microneedle Patches for Diabetes Treatment.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2019 Jan;13(1):41-48. doi: 10.1177/1932296818778607. Epub 2018 May 31. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 29848105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transdermal Insulin Delivery and Microneedles-based Minimally Invasive Delivery Systems.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(39):3175-3193. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220608130056. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 35676840 Review.
Cited by
-
Skin-like hydrogel devices for wearable sensing, soft robotics and beyond.iScience. 2021 Sep 26;24(11):103174. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103174. eCollection 2021 Nov 19. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34755087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Colorimetric Dermal Tattoo Biosensor Fabricated by Microneedle Patch for Multiplexed Detection of Health-Related Biomarkers.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Dec;8(24):e2103030. doi: 10.1002/advs.202103030. Epub 2021 Nov 1. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34719884 Free PMC article.
-
Blue-ringed octopus-inspired microneedle patch for robust tissue surface adhesion and active injection drug delivery.Sci Adv. 2023 Jun 23;9(25):eadh2213. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adh2213. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37343097 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine delivery systems toward lymph nodes.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Dec;179:113914. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.113914. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 34363861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered drug delivery devices to address Global Health challenges.J Control Release. 2021 Mar 10;331:503-514. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.01.035. Epub 2021 Jan 28. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 33516755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ohkubo Y et al. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a randomized prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract 28, 103–117 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Owens DR, Zinman B & Bolli GB Insulins today and beyond. Lancet 358, 739–746 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Bakh NA et al. Glucose-responsive insulin by molecular and physical design. Nat. Chem 9, 937–943 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

